China has been at the forefront of experimenting with a digital currency, with almost 21 million people taking part in digital yuan (e-CNY) tests through June, according to the People’s Bank of China (PBOC). A digital yuan offers better data for the PBOC—China’s central bank—and other government bodies. The more the digital currency is used, the more the government has instant awareness of purchases and transfers, even knowing the geographic location of activity.
Using digital yuan also means greater consumer efficiencies and analytics. Look to a new generation of freemium and bank-linked financial planning and insight activity. The Digital yuan system can make all the payments on many things including transportation, food, and entertainment.
Digital yuan allows for a greater ability to monitor as the Chinese government believes in control. A digital yuan can be used to steer people away from other digital currencies and bitcoin variants, which in turn keeps the data onshore. This control could be equally used to counter money laundering and other illegal activities. The Digital yuan system could also disintermediate other payment mechanisms.
A digital currency gives the yuan greater utility and the PBOC deserves credit for its willingness to experiment. Although there has been significant liberalisation in recent years there are still capital controls in China and the yuan is not freely convertible. The yuan in global finance could become quite significant in the coming decades if China adopts inflation targeting, substantially cleans up its banking system, opens up its capital account and allows its currency to freely float.
The introduction of a digital yuan will bring benefits to Chinese consumers and society, facilitate government data collection and monitoring, but will not have a material impact on the yuan’s international status.
Nonetheless, it poses an interesting question to financial leadership in the U.S. and Europe as to whether they also have the capacity to innovate and experiment. According to an article, China’s sovereign digital currency program, Digital Currency Electronic Payment (DCEP), has launched one of the largest real-world trials in several cities over the last few months. By May 2020, China had already filed more than 120 patent applications for its official digital currency (alternately referred to as digital yuan in this article), more than any other country.
PBOC has given the green light to conduct hypothetical-use tests of the digital yuan in several regions – Beijing-adjacent Xiong’an New Area, Shenzhen, Suzhou, Chengdu, and the Beijing 2022 Winter Olympic Games locations.
In the latest digital currency trials, Suzhou municipal government announced that it would give away 100,000 digital red packets, each containing RMB 200 (US$31) and totalling RMB 20 million (US$3 million), to residents via a lottery. Suzhou has been spearheading the digital currency trails. Since May, some Suzhou government employees have been receiving their transport subsidies in the form of digital currency.
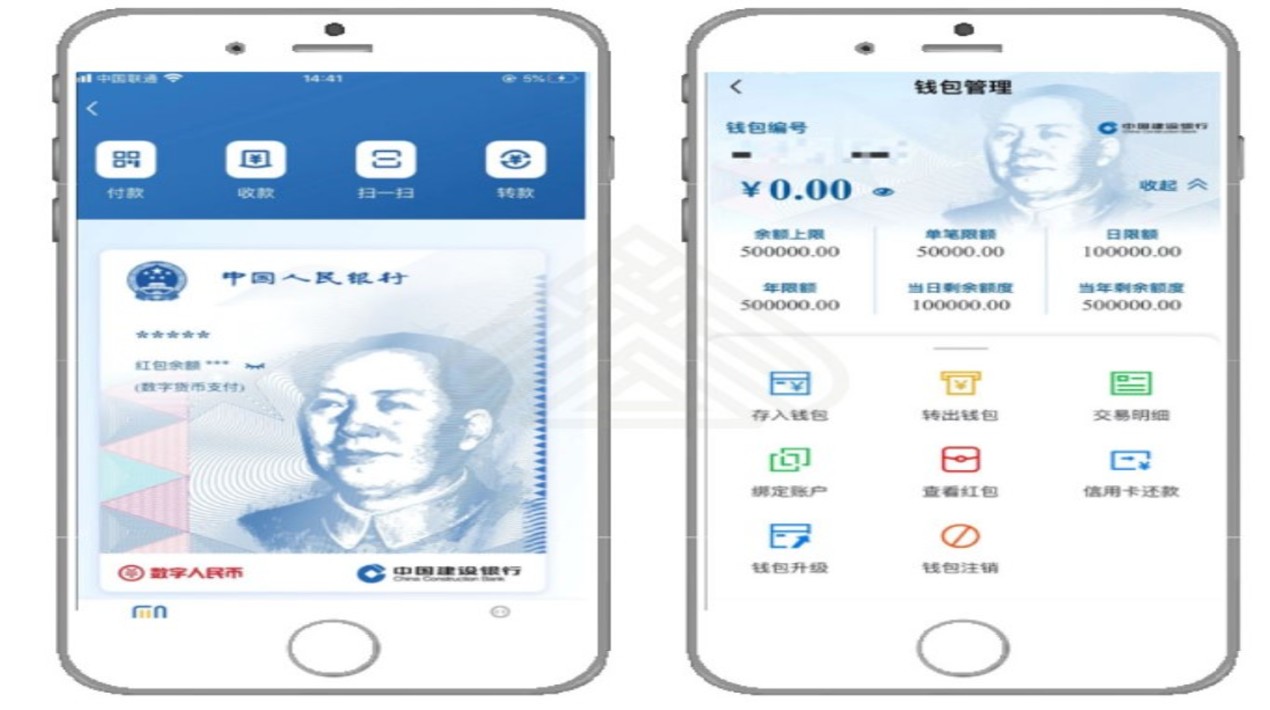
China’s central bank is responsible for issuing and distributing the digital yuan to commercial banks. Commercial banks will then channel the digital money to end users. So far, China’s four major state-run banks – China Construction Bank, Bank of China, Industrial and Commercial Bank of China, and Agricultural Bank of China – have started large-scale internal testing of the digital RMB wallet.
As reported by OpenGov Asia, China’s monetary authorities will designate more payment service institutions to develop digital RMB electronic wallets with complicated functions to satisfy various types of payment needs. The digital RMB e-wallet with smart contracts has a new feature that allows users to implement payment autonomously under certain conditions and rules.
This system can prevent the illegal withdrawal of funds deposited in prepaid accounts. The digital RMB is expected to be one of the world’s first major sovereign digital currencies, and the central bank is gradually expanding its trials.
















