 Leander Werbrouck (Global Director, Product Management Surgical Imaging) has been active for 15+ years in various technology and manufacturing industries, making him a tech-savvy entrepreneur with extensive product and marketing experience. Leander joined Barco’s Entertainment market team in early 2018, taking the lead on the professional AV segments with a clear mission to enable Barco’s customers and industry partners to easily operate and more efficiently create immersive experiences and visitor attractions.
Leander Werbrouck (Global Director, Product Management Surgical Imaging) has been active for 15+ years in various technology and manufacturing industries, making him a tech-savvy entrepreneur with extensive product and marketing experience. Leander joined Barco’s Entertainment market team in early 2018, taking the lead on the professional AV segments with a clear mission to enable Barco’s customers and industry partners to easily operate and more efficiently create immersive experiences and visitor attractions.
In 2020, Leander accepted a new opportunity stepping into the healthcare market as head of the global product management for Barco’s Surgical Imaging business. Together with the team, his focus is on driving the business to innovation and sustainable growth and enabling better healthcare outcomes.
Instant access to everything: information, data, … people
“Instant access” is an adage our entire society lives by, ever since the internet took the idea and made it a reality. On a personal level, friends, shops, music and movies are just a click away. For healthcare professions, electronic patient records and enterprise imaging realise uniform patient files and make it easier to share images in multiple formats within an organisation.
These examples illustrate instant access to information and data, but the Covid-19 crisis proved that connecting to people is just as valuable, if not even more so. People come with more than just factual information or data: they add expertise, experience and a human touch to medical problems. As a result, telemedicine has been boosted in a whole range of ways.
Remote collaboration as a game-changer in surgery
The idea of remote surgical work was originally closely connected to robotic surgery, which has been around for several decades. The concept of ‘telesurgery’ describes the possibility of executing surgeries remotely, with the surgeon and the patient being in different places. The surgeon controls a robot that is with the patient in the OR, and in this way executes the procedure from a distance. The world’s first remote surgery was completed in 2001, a laparoscopic cholecystectomy on a patient in France, performed via a robot by a surgical team in New York.
The idea was that surgeries could be done in this way for areas that are difficult to reach, such as remote rural places, warzones or even on astronauts in space. Still, there are some challenges to robotic telesurgeries, such as a delay in transfer time (referred to as latency), and the absence of haptic feedback. For both, technology is getting better at speeding up transfer times and simulating tactile feedback.
Why virtual representation is perfect for the OR of today and tomorrow
Still, there is more to remote surgery than robotic telesurgery. The question is not always whether the surgeon can reach the patient, sometimes it is about the surgeon being with the patient in the OR, but without access to the experience, they need. Or students being unable to observe a surgery in the actual operating theatre, because it is too far away or because they’re too large in number. In those cases, the surgeon is physical with the patient, but they could use ‘instant access to people who are not there.
Remote work is everywhere already, so why could it not be used in surgery? The situations that lend themselves for it are plentiful:
- Surgeons could consult experts when necessary.
- Novice surgeons could get remote guidance from more experienced colleagues.
- Students could attend more types of interventions, in bigger numbers than what is possible in the physical OR (and each of them getting a front-row seat).
- New technologies and surgical material could be assessed as it’s being used, live.
- Sales representatives from medical device companies could give remote demos, or virtually ‘scrub in’ and accompany the surgeon when they’re using new material for the first time.
- Important surgeries could be conferenced live for an audience.
A virtual presence solution for the OR does away with some of the hassles that come with travel, strict planning, physical restrictions in the OR, and the need to learn to use new technologies and devices quickly.
In short, remote collaboration during surgery offers surgeons a flexible environment for support, consultation and teaching, when and where they need it. Just like office workers hold hybrid meetings with colleagues, and airports and ports offer communication support for pilots and captains, surgeons can use collaboration solutions to maximise their outcomes.
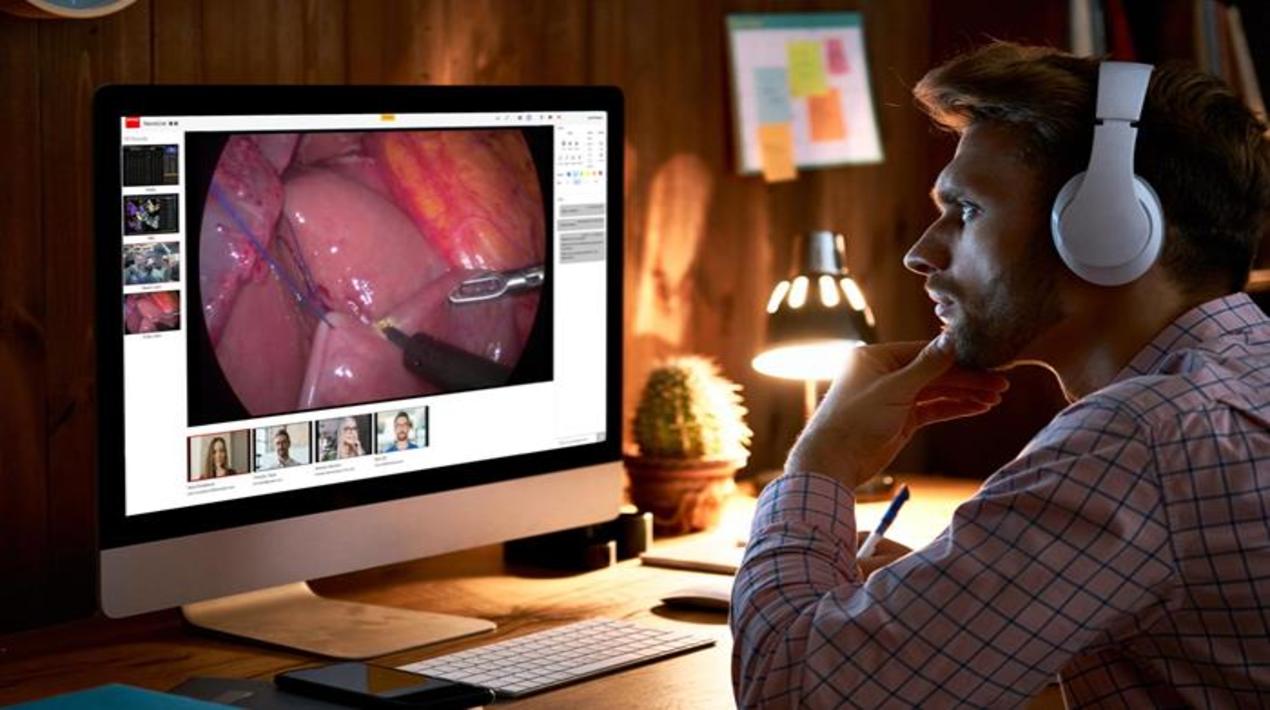
Discover NexxisLive
With NexxisLive, you can involve the right people for any type of intervention, wherever they are. Telestration, teleassistance, teleconferencing, and telementoring: the platform expands your OR, virtually and securely, with real-time video and high-quality audio.
Increase your surgical performance with excellent video quality, minimal latency and capturing options. Whether you are consulting experts, educating students or assisting with technical equipment, you can rely on real-time images, remote communication and bi-directional annotation options designed with the surgeon in mind. It is a flexible platform for any hospital size and any type of surgery.
Read and know more here.