The healthcare industry is changing rapidly; several new companies are entering the industry and are becoming significant contributors to it. Business models of companies are being modified and new partnerships are beginning to emerge.
And all of it is happening because of the Internet of Things and other technologies like cloud-based services and big-data; it is happening because the world is becoming more digital, more connected and more data intensive every day.
Integrated Health Information Systems (IHiS), the public healthcare IT shared services provider and subsidiary of Ministry of Health Holdings (MOHH), helps integrate IT into health care services and operations across Singapore. As the Singapore healthcare ecosystem is fairly complex, there is a great demand for more efficient and expedited services.
IHIS hosts a bevy of tech solutions and gadgets, specifically catered to the health industry. There are different solutions created for patients and healthcare staff. Some of which include:, Outpatient Pharmacy Automated System, Digital Pathology System, Real-Time Ambulatory Patient Information Deployment Enabler (RAPIDE) system, Electronic Health Intelligence System, Tele-Geriatics, Mobile Apps, and other such services.
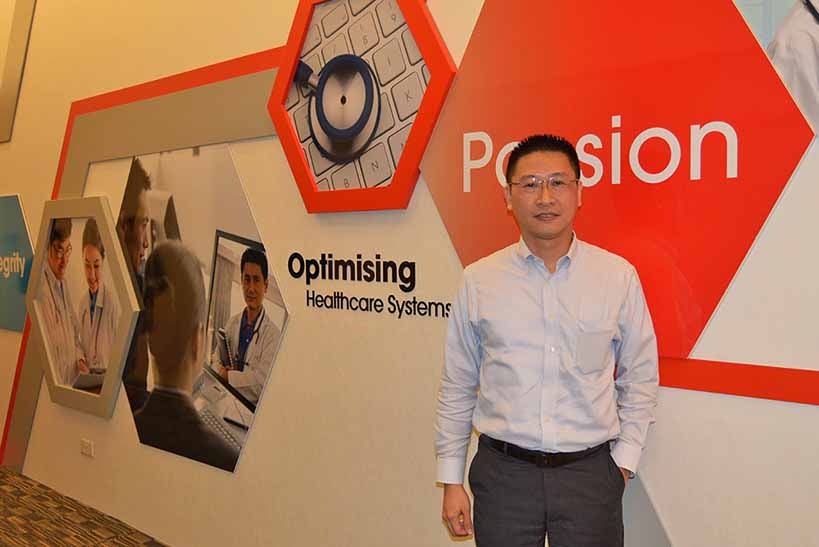
OpenGov recently got the chance to catch up with Mr. James Chia, Director of Corporate Strategy and Business Performance, IHIS, to talk about the Health IT Masterplan, how IHIS is contributing to the Smart Nation vision, and what their plans are, for the near future.
On the Health IT Masterplan
Mr. Chia also holds another portfolio in MOHH, being part of the Health IT Masterplan team. In both his capacities, Mr. Chia can draw alignment between the two bodies, IHIS and MOHH.
Since the Masterplan was conceived less than 2 years ago, it has prepared the health industry for the 2020 vision towards a smart healthcare system.
In arguing how technology can help achieve what is laid out in the Health IT Masterplan, Mr. Chia said, “There are many capabilities identified in the Health IT Masterplan that we need to develop or enhance. These capabilities are at different stages of maturity. For example, Big Data Analytics, with respect to healthcare, is still in the early stages of widespread adoption.” He explains that we can use this information to determine the right level of care for patients across the country.
“Health IT is a critical enabler for the healthcare sector to achieve the 3 objectives of making healthcare in Singapore more affordable, accessible, and of good quality.” said Mr. Chia, “Striving towards a healthy population, we are taking steps to better understand the health of our population. This requires us to learn more about our population segments, who are the people at risk, and for those at risk, how can we intervene early as well as motivate them to stay healthy.”
Mr. Chia shared that Singapore has the highest density of HIMSS EMRAM Stage 6 hospitals in Asia. The HIMSS EMRAM award is an international benchmark for the use of advanced IT to improve patient care. Tracking their progress in completing eight stages (0-7), hospitals can review the implementation and utilisation of information technology applications with the intent of reaching Stage 7, which represents an advanced electronic patient record environment. Currently, there are 25 acute care facilities in Asia Pacific at Stage 6 and three at Stage 7. Explaining that achieving IT excellence in hospitals is not an end itself, “We are moving away from episodic care towards care delivery that is coordinated around the patient. That is why we need ensure that our clinicians and medical staff will be adequately IT equipped regardless which care setting the patient turns up in.” says Mr. Chia, “In other words, our scope and efforts include primary care, intermediate and long term care, in addition to acute hospital care.”
“What is fundamental for this to work? Information flow. Right now, we are in the midst of enabling seamless flow of patient information across the healthcare providers. Beyond this, to make this vision work, we must make sure the providers know enough about the patients such that repeated questions and tests can be avoided, allowing doctors to spend more time on diagnosis and treatment while saving patients time and money.
Aligning to the Health IT Masterplan, IHIS is looking at progressively providing more common platforms across care providers and patients for greater interoperability and unified user experience. “This would ensure that the information collected within the community, can form part of a continuity of care record around each patient. In case of an emergency, such information can be accessed so that the attending doctor can be adequately informed and appropriate care can be delivered to the patient.”
How do you plan to use data?
The partnership between IHIS and big data analytics is in a nascent stage but they are looking to develop this very rapidly. Through the Electronic Health Intelligence System (eHINTS) and Business Information (BI) System, they are hoping to facilitate more informed decision making, improve operational efficiency, resource allocation and cost management.
To consolidate data, the eHINTS system cleanses and standardises data before uploading for decision-support, while the BI System classifies data by subject areas to prepare for analysis. “IHIS is focusing our efforts to harness intelligence and insights from our wealth of data to improve clinical care and operations. First, we try to make sure we provide the data in as much of a uniform manner as possible,” Mr. Chia tells us.
“From there, statistical analysis and techniques like data mining, scenario modeling can play a big difference in how we make care more effective and more efficient,” Mr. Chia said.
“Undergirding all that, we need to have integrated systems that pull the right information from multiple credible sources in a timely manner,” stated Mr. Chia, “Then we can turn that data into insights to help both our management team and frontline colleagues make informed decisions.”
Health Mobile Apps and Service Virtualisation
Service virtualisation is an area where IHIS has introduced several mobile platforms to cater to healthcare needs. Their range of mobile applications includes AsthmaCare Buddy, Thought Buddy, iCom, Patient Communicator, miHealthcare, Nurses Pal, and GPFirst Aide.
IHIS sees mobile apps as an area they can use to ‘nudge’ people towards behaviours that promote healthier living, due to the rise of mobile activity. The use of behavioural science and gamification create these opportunities for interactive and responsive patient actions.
For example, the Gacha Island app features games that simulate “killing” of monsters (substituting for mental illnesses). This conveys that people need an arsenal of tools, such as social support, to deal with mental health issues. Another app, called MyEyeDrops, reminds glaucoma and cornea patients to apply eye drops and medication. MyEyeDrops also keeps a diary to record the frequency and intensity of their disease to facilitate management by their doctors.
IHIS has also developed mobile apps to give support to Healthcare staff. Nurses Pal, for example, helps nurse aids more quickly adjust patients’ intravenous drips, manage bedsores and prevent falls.
IHIS is driven towards greater service virtualisation as they foresee it will help optimize the land space at hand. Singapore is not a large nation, this requires us to utilise our resources to the best of their ability. Service virtualisation and mobile app service delivery allows this to happen.
“This should be transparent to the consumer in most cases,” Mr. Chia asserts, “As a system it is quite important, considering the scarce resources we have today. Virtualisation of services allows for the scale up of capabilities and capacities without incurring more land space or more resources. At the same time we are optimising the land space, today’s technology can allow the same hardware to run multiple servers, applications, service resources, and all within the same land space.”
Impact on Citizens of the Future
In relation to Smart Nation, one objective of IHIS is to help empower the people of Singapore. This means that Smart Health should be proactively delivered, integrated, and personalized. Through these factors, an individual will be empowered to take healthcare into their own hands.
“We want people to not only live longer, but also healthier,” said Mr. Chia. Mr. Chia implores how the health industry can motivate and equip people with the right tools to think about daily health decisions. “We are hoping that we can move into the age where long gone will be the days where we are heavily dependent on others for our own health and well-being,” says Mr. Chia.
Today, we are already living in a healthcare system of the future. Our calendar alerts and online health records are just two ways that we access healthcare resources through technology. IHIS is directing its efforts towards capitalizing on the added advantage of integrating technology into the healthcare system.
Since 2008, IHIS has been raising the bar when it comes to bringing technology in clinical spaces. As Mr. Chia puts it, technology is not an end in itself, improving the health of our people is at the heart of all we do. IHIS continuously try to help the country ‘move forward in unison’ by leveling up IT capabilities in our healthcare organisations so that we can deliver citizen-centred care as one national healthcare system.