Due to COVID-19, access to the operating theatres in hospitals is restricted, which means medical training must balance practical learning experiences while ensuring the safety of their students.
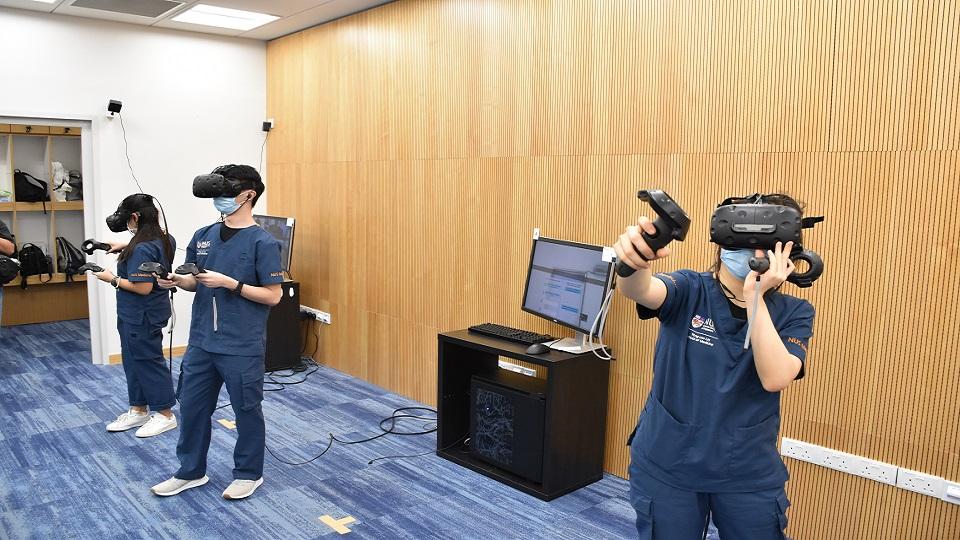
NUS have released how they are enabling their medical students from the NUS Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine to experience the process of patient safety and immersion in operating theatre procedures through virtual reality (VR).
The students have been able to learn about the entire flow of the peri-operative setting: from dental clearance to anaesthesia evaluation, to the handling of sharps during surgery and the safe conduct of operations in a simulated environment through VR headsets and hand-held controllers.
The system, called PAtient Safety aS Inter-Professional Training (PASS-IT), is a digital gamified environment that allows students to learn about hands-on techniques in the operating theatre.
“PASS-IT’s gamified style lets multiple learners be immersed in situations where they are given the opportunity to participate in what would usually be a highly restricted environment,” said Associate Professor Alfred Kow, a surgeon and Assistant Dean (Education) of NUS Medicine.
“With the COVID-19 situation, students have also been removed from these settings of practical learning due to the risk of exposing them to aerosol-generating procedures. This VR system is a good tool to help the students consolidate their learning despite increased clinical restrictions,” he added.
Operating in the virtual training world
Medical students use VR headsets and hand-held controllers to interact with each other in real-time. Their physical movements and actions are also tracked and displayed in real-time for visualisation and evaluation.
The tool allows students “to make mistakes, learn in a safe environment and ensure that they are competent before they enter actual clinical environment to care for patients”, according to Assoc Prof Kow.
The PASS-IT programme was piloted with a cohort of 36 third-year medical students who had just completed their clinical rotations in surgery, as well as 56 fourth-year medical students during their Phase IV Anaesthesia posting.
Students showed improved understanding of peri-operative patient safety after the training. Results also showed that the VR training had elevated the students’ appreciation for effective communication between healthcare workers, and the majority of students also spoke positively of the use of VR technology to enhance their knowledge of patient safety.
Assistant Professor Terry Pan from the Department of Anaesthesia at NUS Medicine said the introduction of the PASS-IT VR system has been timely as it gave the students “a unique opportunity to continue the operating theatre learning experience virtually in a safe and structured manner”.
“This innovative VR tool can certainly complement the operating theatre learning experience when the current restrictions are lifted,” he added.
Photo Credit:https://news.nus.edu.sg/