By examining how the microphysics of collisionless plasmas affects macroscopic astrophysical processes, researchers at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) have developed a new paradigm for understanding the origins of magnetic fields.
The research was made possible by the National Science Foundation (NSF) of the United States of America elaborated on the theory that underlies the phenomenon and carried out numerical simulations on supercomputers to demonstrate how macroscopic magnetic fields can be seeded in addition to the fundamental processes that are taking place. The model replicates magnetogenesis on a cosmological scale.
People can now start to figure out how the universe got its magnetic fields, which they can see with the Event Horizon Telescope around supermassive black holes and the Solar Telescope as well, according to Vyacheslav (Slava) Lukin, Program Director, NSF’s Division of Physics.
Magnetic fields can be found anywhere, even in the vast space between galaxies and clusters of galaxies, where there is nothing but emptiness. Even after decades of intense study and research, cosmologists still don’t know where these mysterious magnetic fields come from.
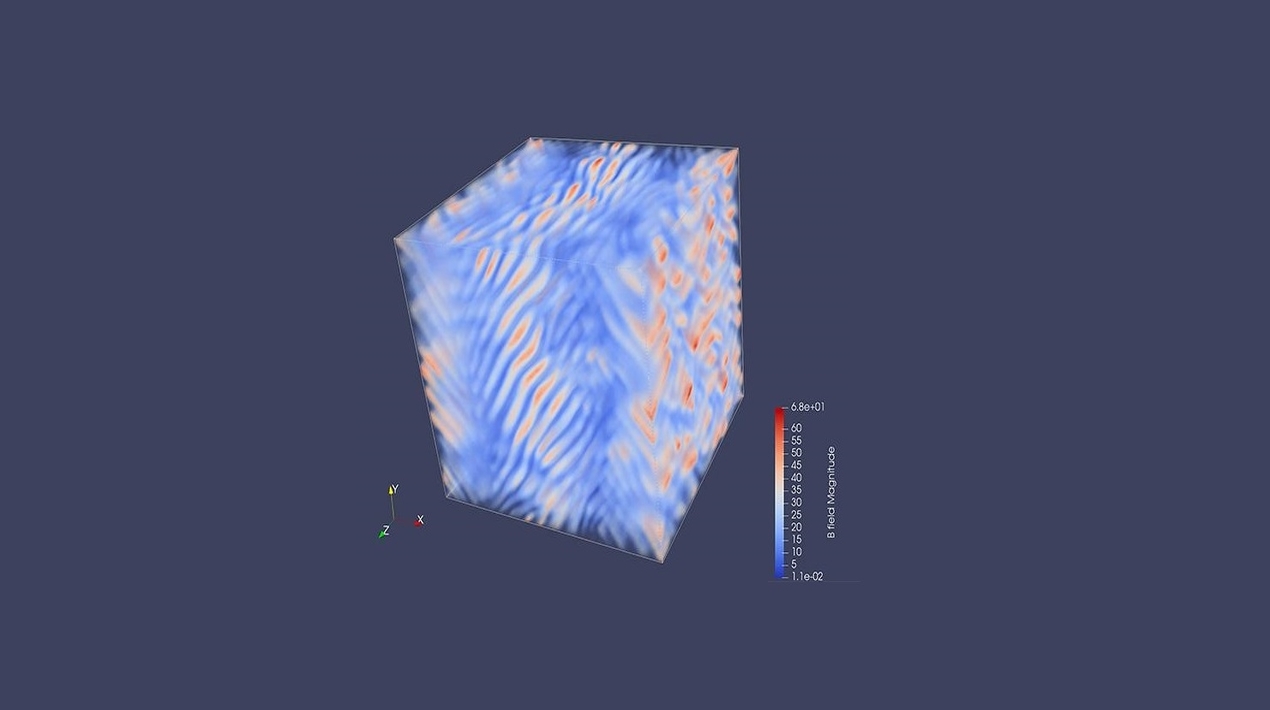
Plasmas between stars and galaxies are not very dense. This means that in cosmological plasmas, the particles never touch each other. This is a key property that the researchers put into their model. The model shows that flows in plasma that don’t hit each other can make magnetic fields on their own. It does this by showing how small-scale plasma dynamics affect large-scale astrophysical processes.
Because they are made by the mechanical energy of turbulent motion, magnetic fields can change how plasma moves. The team wrote about what they found in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Furthermore, the study is a step toward figuring out what makes magnetogenesis happen in the universe. Astronomical observations show that magnetic fields that are dynamically important are all over the Universe, but nobody knows where they come from.
This work shows how the effects of the microphysics of collisionless plasmas on large-scale astrophysical processes can help us figure out where cosmic magnetism comes from. The study shows that the first magnetic fields can be made by generic motions of astrophysical turbulence using kinetic plasma physics. This means that all plasmas in the universe are magnetised.
The theoretical and numerical results set the stage for figuring out how these “seed” magnetic fields are further amplified by the turbulent dynamo, which is another important and long-standing question. This helps move forward a fully self-consistent explanation of how cosmic magnetogenesis happens.
Researchers had looked at the creation of “seed” magnetic fields by the Weibel instability in an initially unmagnetised plasma driven by a large-scale shear force. This was done in a fully kinetic framework. They make an analytical model that shows how phase mixing causes thermal pressure anisotropy, how magnetic fields then grow exponentially in the linear Weibel stage, and how the Weibel instability ends when the seed magnetic fields are strong enough to make particles spin around and stop them from moving freely.
Simulations of a two-dimensional and a three-dimensional electron-positron plasma using the particle-in-cell method confirm that the predicted scaling dependences of the saturated fields on key parameters like the ratio of system scale to electron skin depth and forcing amplitude are correct.
This work shows that a collisionless plasma can become magnetic on its own through large-scale motions as simple as a shear flow. This has important implications for how magnetism forms in astrophysical systems with few particles.
















