The International Telecommunication Union (ITU) – the United
Nations specialised agency for information and communication technology, has published a new
assessment on global electronic waste (e-waste), policies and statistics, The Global E-Waste Monitor 2017.
The report was released by ITU together the United Nations
University (UNU) and the International Solid Waste Association (ISWA). The
report seeks to increase global awareness and draw attention to the growing
world issue of e-waste.
Electronic waste, or e-waste, refers to all items of
electrical and electronic equipment (EEE) and its parts that have been
discarded by its owner as waste without the intent of re-use. This includes
discarded products with a battery or plug including mobile phones, laptops,
televisions, refrigerators and electrical toys.
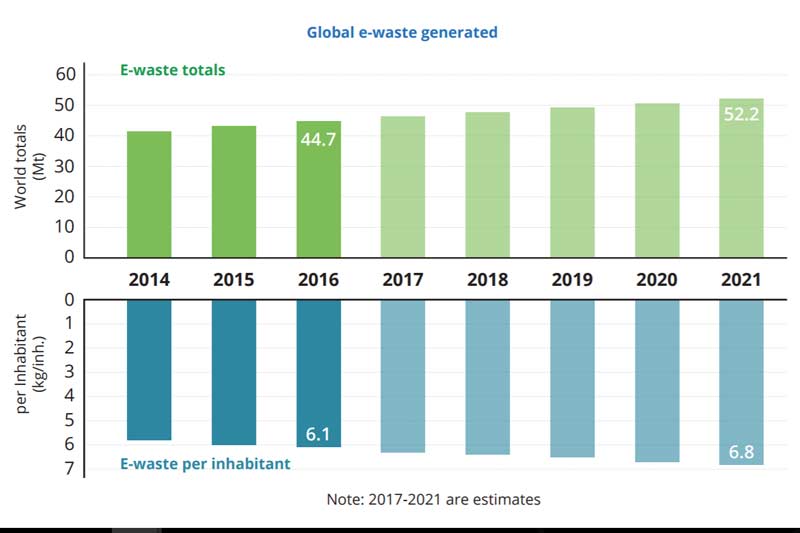
The assessment found that in 2016, 44.7 million metric
tonnes (Mt) of e-waste were generated, increasing by 3.3 million metric tonnes
(8 per cent) from 2014. In 2016, only about 20 per cent – or 8.9 million
metric tonnes – of all e-waste was recycled. Experts foresee a further 17 per
cent increase — to 52.2 million metric tonnes of e-waste by 2021.
The growing amount of e-waste is the result of multiple
trends. Rapid technological advances are driving innovation, efficiency, and
social and economic development and there is an increasing number of users of
ICT (information and communication technology) and. By 2017, close to half the
world’s population uses the internet and most people in the world have access
to mobile networks and services. Many people own more than one ICT device, and
replacement cycles for mobile phones and computers, and also for other devices
and equipment, are becoming shorter. At the same time, disposable incomes in
many developing countries are increasing and a growing global middle-class is
able to spend more on electrical and electronic equipment. Current trends
suggest that the amount of e-waste generated will increase substantially over
the next decades, and that better data to track these developments are needed.
In 2016, Asia generated the largest amount of e-waste (18.2
Mt), followed by Europe (12.3 Mt), the Americas (11.3 Mt), Africa (2.2 Mt), and
Oceania (0.7 Mt). While the smallest in terms of total e-waste generated,
Oceania was the highest generator of e-waste per inhabitant (17.3 kg/inh), with
only 6% of e-waste documented to be collected and recycled. Europe is the
second largest generator of e-waste per inhabitant with an average of 16.6
kg/inh but it has the highest collection rate (35%). The Americas generate 11.6
kg/inh and collect only 17% of the e-waste generated in the countries, which is
comparable to the collection rate in Asia (15%). However, Asia generates less
e-waste per inhabitant (4,2 kg/inh). Africa generates only 1.9 kg/inh and
little information is available on its collection rate. The report provides
regional breakdowns for Africa, Americas, Asia, Europe, and Oceania.
The assessment also highlights the significant and growing
risk to the environment and human health due to increasing levels of e-waste
and its improper and unsafe treatment and disposal through burning or in
dumpsites. Dismantling processes that do not utilise adequate means,
facilities, and trained people pose additional threats to people and the
planet. This presents challenges to the achievement of SDGs (Sustainable Development
Goals) related to environmental protection (Goals 6- clean water and sanitation,
11 -sustainable cities and communities, 12, and 14- life below water) and
health (Goal 3).
The assessment notes the positive news that there is
now a growing number of countries adopting e-waste legislation. Currently 66
per cent of the world population, living in 67 countries, is covered by
national e-waste management laws, a significant increase from 44 per cent in
2014. National e-waste policies and legislation play an important role as they
set standards, guidelines and obligations to govern the actions of stakeholders
who are associated with e-waste.
The large increase was mainly attributed to India, where
legislation was adopted in 2016. The most populous countries in Asia currently
have e-waste rules, whereas only a handful of countries in Africa have enacted
e-waste-specific policies and legislations. However, the report also says that
countries with national e-waste management laws do not always enforce the law.
Many countries lack measureable collection and recycling targets that are
essential for effective policies.
The assessment also reports that low recycling rates can
have a negative economic impact, as e-waste contains rich deposits of gold,
silver, copper, platinum, palladium and other high value recoverable materials.
It estimates that the value of recoverable materials contained in e-waste
generated during 2016 was US $55 billion, which is more than the Gross Domestic
Product of most countries in the world.
ITU recommends that circular economy models be adopted to
encourage closing the loop of materials through better design of components,
recycling, reusing, etc., while mitigating the environmental pollution.
Earlier this year ITU, UNU and ISWA joined forces and
launched the "Global
Partnership for E-waste Statistics". Its objective is to help
countries produce e-waste statistics and to build a global e-waste database to
track developments over time. This partnership further aims to map recycling
opportunities from e-waste, pollutants and e-waste related health effects,
along with building national and regional capacities to help countries produce
reliable and comparable e-waste statistics that can identify best practices of
global e-waste management.
ITU Secretary-General, Houlin Zhao said, “E-waste management
is an urgent issue in today's digitally dependent world, where use of
electronic devices is ever increasing – and is included in ITU's Connect 2020
Agenda targets. The Global E-waste Monitor serves as a valuable resource
for governments developing their necessary management strategies, standards and
policies to reduce the adverse health and environmental effects of e-waste –
and will help ITU members to realise this Connect 2020 target."
"With 53.6 per cent of global households now having
Internet access, information and communications technologies are improving
peoples' lives and empowering them to enhance their social and economic
well-being," said Brahima Sanou, Director of the ITU Telecommunication
Development Bureau. "The Global E-Waste Monitor represents an important
step in identifying solutions for e-waste. Better e-waste data will help
evaluate developments over time, set and assess targets, and contribute to
developing national policies. National e-waste policies will help minimise e-waste
production, prevent illegal dumping and improper treatment of e-waste, promote
recycling, and create jobs in the refurbishment and recycling sector."
"The world's e-waste problem continues to grow.
Improved measurement of e-waste is essential to set and monitor targets, and
identify policies," said Jakob Rhyner, Vice-Rector of the United Nations
University. "National data should be internationally comparable,
frequently updated, published and interpreted. Existing global and regional
estimates based on production and trade statistics do not adequately cover the
health and environmental risks of unsafe treatment and disposal through
incineration or landfilling."
While Antonis Mavropoulos, President of the International
Solid Waste association (ISWA), commented, "We live in a time of
transition to a more digital world, where automation, sensors and artificial
intelligence are transforming industry and society," "E-waste is the
most emblematic by-product of this transition and finding the proper solutions
for e-waste management is a measure of our ability to utilise the technological
advances to stimulate a sustainable future and to make the circular economy a
reality. We need to be able to measure and collect data and statistics on
e-waste, locally and globally, in a uniform way. This report represents a
significant effort in the right direction and ISWA will continue to support it
as a very important first step towards the global response required."
Access the complete report here.
















