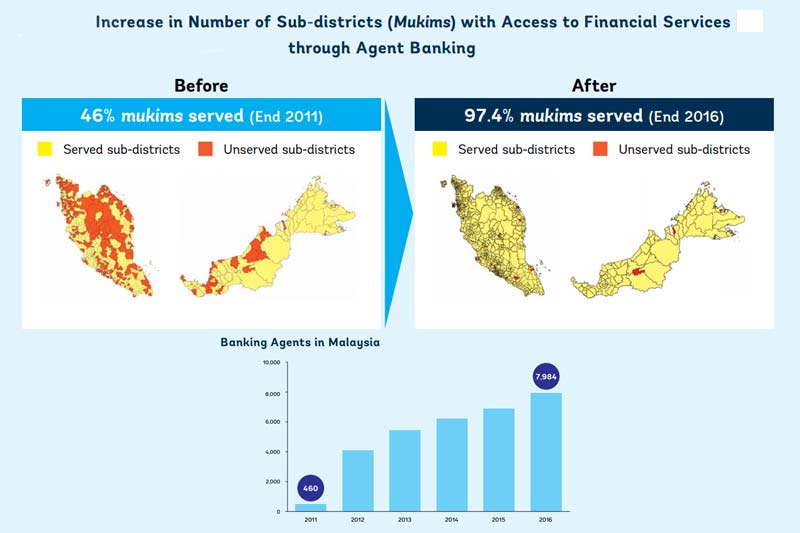
Image from World Bank report (Original source of statistics: Bank Negara Malaysia)
Malaysia has achieved one of the highest levels of financial inclusion among middle-income countries. According to data from the central bank, 92% of the adult population in Malaysia had a bank account in 2015, the second highest rate in ASEAN after Singapore.
The World Bank published a report in May 2017, titled ‘Financial Inclusion in Malaysia: Distilling Lessons for Other Countries’, to identify the reforms and actions undertaken by Malaysia to drive financial inclusion. The third section of the report looks at Malaysia’s experience with “agent banking”, which leverages technology to provide financial services to under-served population.
The central bank of Malaysia, Bank Negara Malaysia (BNM) gained the legal authority to proactively promote financial inclusion with an amendment in the Central Bank of Malaysia Act in 2009. As part of the Financial Sector Blueprint (FSBP) launched in 2011, BNM designed a comprehensive Financial Inclusion Framework (FIF) setting specific and measurable outcomes, strategies and actions to advance financial inclusion. The FIF consisted of 10 high-impact initiatives, including agent banking (AB), to extend access to financial services to the remaining segments of the population during the period from 2011 to 2020.
BNM launched the framework for AB in August 2012 to reach the the population living in rural areas which have no bank branches.
Each of the selected retail stores or agents receive a POS device/terminal that is connected online real-time with the back-end system of the financial institution (FI). Through this terminal, the agents can offer basic financial services to customers on behalf of the FI, such as opening savings accounts, deposit or withdraw money, making bill and loan payments, making domestic fund transfers, etc.
All three parties benefit from the system. The customers are able to access financial services without expending time and monetary resources in travelling to distant access points. The FIs can expand their customer base with significantly lower investment and maintenance than a traditional brick and mortar branch or even an automated teller machine (ATM) would require. The agents earn additional income from the commissions on the financial transactions and the increased footfall in their premises can provide a boost to their core business.
BNM designed the regulations to protect customers and ensure that there is clear assignment of responsibility.
The regulations ensure that the agent is only the touch point. The information is channeled to banks’ back-end and banks perform the customer due diligence (CDD) against their own database.
FIs are accountable for all services that agent banks perform on their behalf. Agents must receive training from the FIs on areas such as products, services, protection of customer information fraud detection mechanism, AML/CFT (Anti-money laundering/ Countering Financing of Terrorism), equipment operation and complaints handling. The selected agents must have a valid business license, and pass a thorough due diligence process in order to assess their credit profile, business owner reputation, and capability and competency to provide AB services.
Approval of the customers’ application for the opening of savings accounts and issuance of ATM/debit cards is done by FIs. Agent banks facilitate a standardized preliminary Know-Your-Customer (KYC) procedure that consists of collecting customers’ KYC information via an online-real time system of the FI and verification of customers’ identities via the national identification card (MyKad) and a biometric authentication. For debit card transactions a third verification takes place with the entering of the personal identification number (PIN). The customers’ information is screened against several databases in order to comply with the AML/CFT requirements.
The provision of ABl services is restricted only to unserved and underserved areas for Malaysian citizens. Underserved areas are identified based on sub-districts (mukims) with a population of more than 2,000 or in the case of Sabah, Dewan Undangan Negeri (DUNs), which have no more than five access points. During the initial phase of AB, only a limited number of financial services were allowed, which was extended in 2015, in response to demand from customers and agents.
The information of appointed agents and other transactions such as deposits, withdrawals, and payments are also filed to BNM. All participating FIs are required to submit a monthly report to BNM that includes the number of agents opened, and total amount of transactions. Furthermore, FIs are required to send an active accounts report in order to monitor the level of usage and new savings accounts opened. The reports sent to BNM also include updates the status on agents that were reported to the police for inappropriate business practices.
In 2011, only 46% of the sub-districts in Malaysia had access to financial services. Three years after AB was implemented, that number had increased to 97%.
Three Development Financial Institutions, National Savings Bank or Bank Simpanan Nasional (BSN), Bank Rakyat, and Agrobank acounted for 94% of all agent banks in the country. BSN accounted for 80% of transactions. Bill payments accounted for 63% of total number of transactions and 61% in value from inception to launch. Opening of new savings accounts remain modest. The World Bank report states that as people become more familiar with agent banking, this product has the potential to promote active use of accounts and to become the distribution channel of a wider variety of financial services such as micro-financing and micro-insurance among the population in rural areas.
This is an excellent example of utilising technology and working with the private sector to achieve a public good, ensuring that the desired objectives are achieved through well-designed regulations.
The World Bank report cautions that there is no single factor or silver bullet to explain Malaysia’s success in financial inclusion. The progress that Malaysia has achieved is the result of efforts undertaken by authorities and the financial sector industry over the past 20 years.
Click here to read about all the comprehensive plans and all the measures.