|
Getting your Trinity Audio player ready...
|
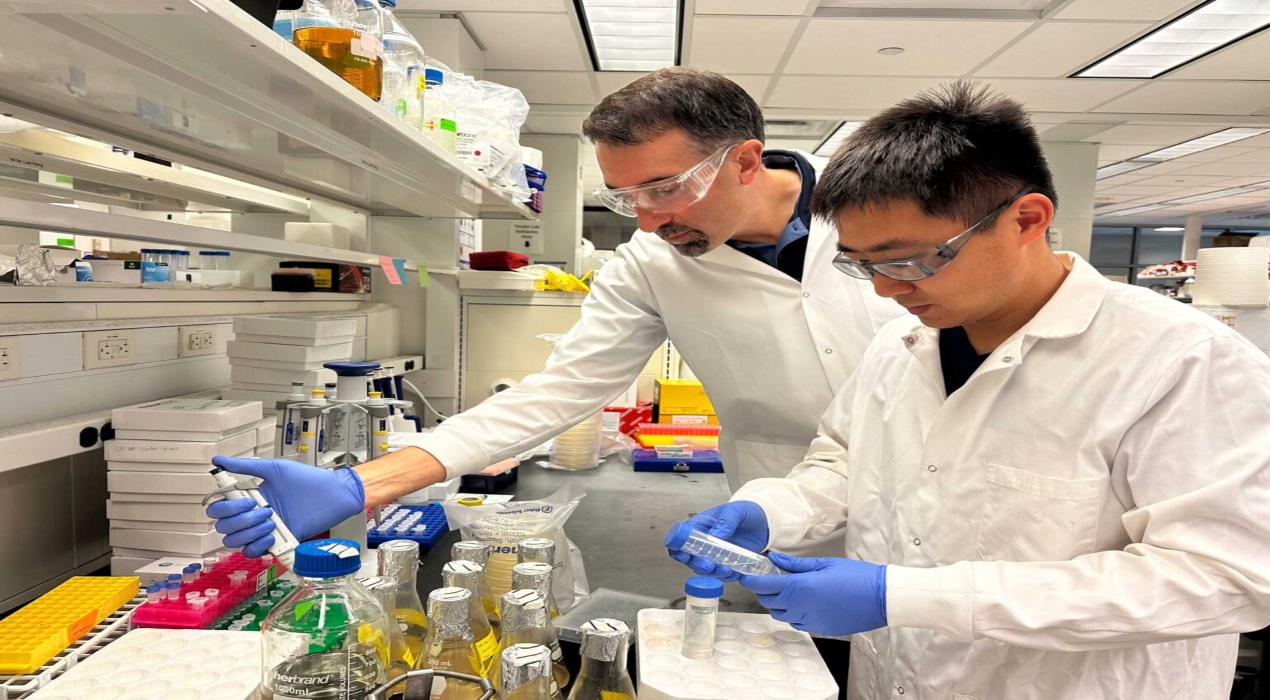
The University of Michigan has developed machine-learning algorithms technology. This new technology can identify problematic areas in antibodies, making them less susceptible to binding non-target molecules. This innovative development, led by Peter Tessier, the Albert Mattocks Professor of Pharmaceutical Sciences at U-M and the study’s corresponding author in Nature Biomedical Engineering, presents a ground-breaking solution to enhance the effectiveness of antibodies in fighting diseases.
“Antibodies play a crucial role in our immune system’s defence mechanism by binding to specific molecules known as antigens on disease-causing agents, such as the spike protein on the COVID-19 virus,” Tessier expressed, “Once bound, antibodies either directly neutralise harmful viruses or cells or signal the body’s immune cells to take action.”
However, there’s a challenge associated with antibodies designed to bind strongly and rapidly to their specific antigens. These antibodies may also bind to non-antigen molecules, leading to their premature removal from the body. Moreover, they can interact with other antibodies of the same type, forming dense solutions that do not easily flow through the needles used for delivering antibody drugs.
Tessier highlighted the importance of antibodies that can simultaneously perform three critical tasks: tightly binding to their intended target, repelling each other, and disregarding other substances within the body. Antibodies failing to meet all three criteria are unlikely to be successful drugs. Unfortunately, a significant number of clinical-stage antibodies fall short in this regard.
In their recent study, Tessier’s team assessed the activity of 80 clinical-stage antibodies in the laboratory. It made a startling discovery – 75% of these antibodies interacted with the wrong molecules, with each other, or both. To address this issue, the team turned to machine learning.
By making subtle changes to the amino acids that make up an antibody, they can alter the antibody’s three-dimensional structure. This modification helps prevent antibodies from behaving improperly, as an antibody’s structure determines the substances it can bind to. However, making changes without careful consideration can introduce more problems than they solve, and the typical antibody contains hundreds of amino acid positions that could be altered.
Fortunately, machine learning offers a streamlined solution. Tessier’s team created models that are trained using experimental data collected from clinical-stage antibodies. These models can precisely identify how to modify antibodies to ensure they meet all three criteria mentioned earlier, with an impressive accuracy rate of 78% to 88%. This approach significantly reduces the number of antibody modifications that chemical and biomedical engineers need to produce and test in the lab.
Tiexin Wang, a doctoral student in chemical engineering and a co-author of the study, emphasised the pivotal role of machine learning in accelerating drug development. This advanced technology is already attracting attention from biotech companies, which recognise its potential for optimising the development of next-generation therapeutic antibodies.
Tessier concluded by mentioning that some companies have developed antibodies with desirable biological activity but are aware of potential challenges when using these antibodies as drugs. In such cases, Tessier’s team steps in to identify specific areas within the antibodies that require modification, offering valuable assistance to these companies.