|
Getting your Trinity Audio player ready...
|
A nation, Vietnam, well-known for its vibrant economy and youthful population, is poised to seize the transformative potential of generative artificial intelligence (GenAI). The country’s vigorous uptake of cutting-edge technology creates an ideal environment for GenAI’s development and implementation.
 The Nation Survey 2023 highlighted Vietnam as a frontrunner in embracing GenAI, with an impressive 91% of surveyed individuals expressing interest in the technology, the highest among all markets surveyed. This enthusiasm positions Vietnam at the forefront of GenAI adoption, promising significant opportunities for growth and innovation.
The Nation Survey 2023 highlighted Vietnam as a frontrunner in embracing GenAI, with an impressive 91% of surveyed individuals expressing interest in the technology, the highest among all markets surveyed. This enthusiasm positions Vietnam at the forefront of GenAI adoption, promising significant opportunities for growth and innovation.
According to recent data, the Vietnamese generative AI market is projected to reach US$153.80 million by 2024, with an anticipated annual growth rate (CAGR 2024-2030) of 23.20%. This growth trajectory is expected to result in a market volume of US$537.70 million by 2030.
Despite the significant growth of generative AI, industry leaders are proceeding with caution in its adoption. Multiple constraints, including cybersecurity concerns, privacy considerations and the complexities of governance and compliance, contribute to this guarded approach.
According to a study by IBM IBV, 84% of executives see cybersecurity risks as the main hurdle to adopting generative AI. The concerns surrounding generative AI-generated threats are particularly pronounced in Vietnam, given the country’s ongoing cybersecurity challenges.
The National Cyber Security Centre (NCSC) reported a significant surge in cyberattacks in 2023, recording a notable 13,900 incidents. This alarming statistic indicates a worrisome increase of 9.5% from the previous year, positioning Vietnam as the third highest in Southeast Asia for the number of cyberattacks.
Additionally, the use of generative AI applications can heighten data and privacy risks due to their reliance on large language models and the generation of new data. This introduces vulnerabilities such as bias, poor data quality, and risks of unauthorised access.
 Given the security risks inherent in generative AI technology, organisations must bolster their cyber defences to safeguard valuable assets. Proactively addressing these concerns is pivotal for ensuring a safe and successful deployment. Careful consideration and robust measures are needed to ensure data and privacy protection throughout the AI lifecycle.
Given the security risks inherent in generative AI technology, organisations must bolster their cyber defences to safeguard valuable assets. Proactively addressing these concerns is pivotal for ensuring a safe and successful deployment. Careful consideration and robust measures are needed to ensure data and privacy protection throughout the AI lifecycle.
In Vietnam’s current landscape, organisations must enhance their protection against generative AI-related threats. Developing strategies and effective measures to address and mitigate these challenges is paramount.
To ensure the security of generative AI usage and readiness for AI integration, organisations should implement robust encryption and access controls. Additionally, clear incident response protocols and continuous monitoring are crucial for swiftly addressing potential security threats to AI training data. These measures enhance defence against unauthorised access, protecting the integrity and confidentiality of AI training data.
Deploying advanced anomaly detection algorithms is crucial for securing AI model usage by identifying potential data or prompt leakage. Real-time alerting mechanisms for evasion, poisoning, extraction, or inference attacks also bolster overall defence against malicious activities, ensuring robust protection of AI systems.
To strengthen defences against emerging threats, organisations can utilise behavioural defences and multi-factor authentication to guard against new AI-generated attacks such as personalised phishing, AI-generated malware, and fake identities. Incorporating these proactive security measures enhances resilience and effectively mitigates the evolving landscape of AI-driven threats, ensuring a strong and adaptive security posture.
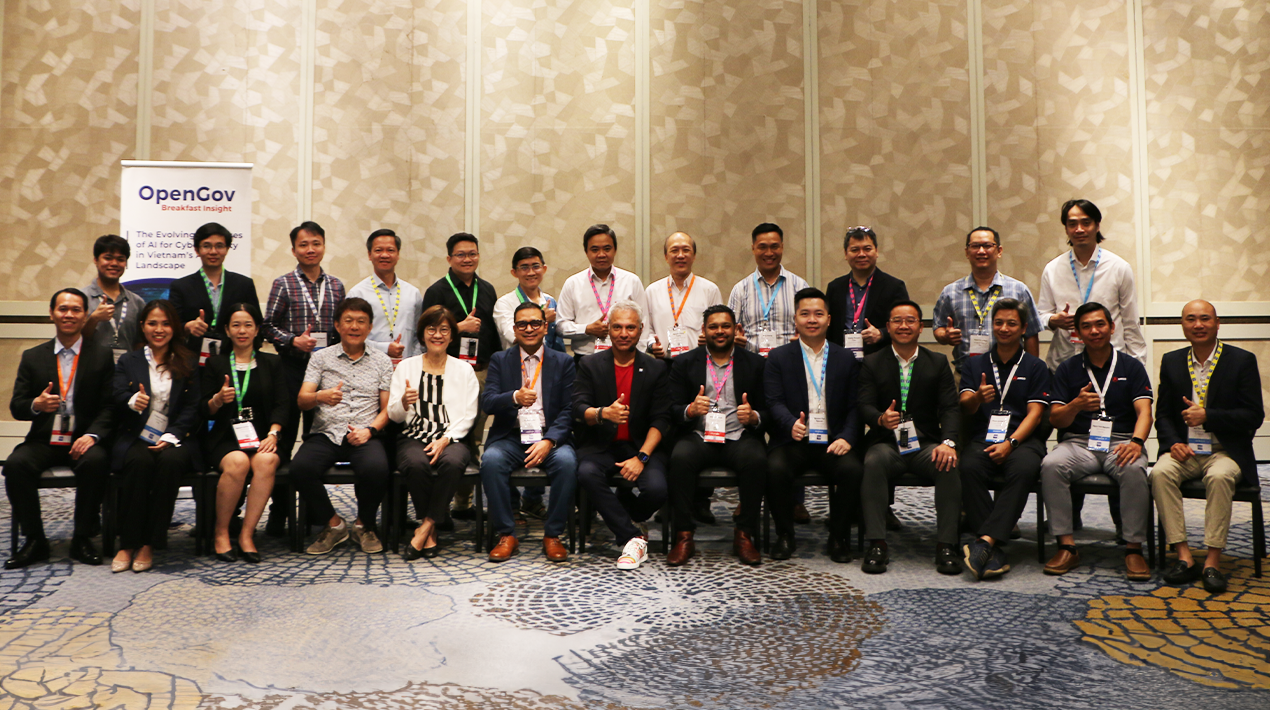
In the uncertain and evolving GenAI landscape, organisations are actively seeking trustworthy technology partners to collaboratively develop and implement secure strategies. The OpenGov Asia Breakfast Insight on 19 March 2024 at Sofitel Saigon Plaza Vietnam, delved into the latest trends and challenges in cybersecurity, particularly in the context of Vietnam’s adoption of generative artificial intelligence (GenAI).
Experts and industry leaders discussed the importance of implementing robust security measures, such as behavioural defences and multi-factor authentication, to mitigate emerging threats like personalised phishing, AI-generated malware, and fake identities. These discussions were vital to maintaining a resilient and adaptable security posture in the era of AI.
Opening Remarks

Artificial Intelligence (AI) is rapidly emerging as a transformative force in today’s landscape, with 84% of organisations citing cybersecurity risks as the primary obstacle to its adoption. Mohit Sagar, CEO and Editor-In-Chief of OpenGov Asia emphasised the importance of navigating the evolving regulatory landscape and AI governance frameworks to mitigate these risks.
However, even though there has been a significant expansion of generative AI, organisations are moving carefully. This tentative approach is due to many issues, including cybersecurity, privacy and the complexity, and sometimes ambiguity, of governance and compliance.
“In Vietnam, the apprehension surrounding AI-generated threats is particularly elevated due to the country’s ongoing cybersecurity challenges,” Mohit asserts. “Securing Artificial Intelligence is of paramount importance as it safeguards against potential threats that can compromise data integrity, ethical considerations, and the overall trustworthiness of AI systems.”
In 2023, the National Cyber Security Centre (NCSC) reported a significant surge in cyberattacks, reaching 13,900 incidents. This alarming statistic signifies a worrisome 9.5% increase from the previous year, positioning Vietnam as the third highest in Southeast Asia for the number of cyberattacks.
Cyber solutions are poised to lead the market, with a projected volume of US$204.60 million in 2024. Looking ahead, the cybersecurity market in Vietnam is expected to witness a robust CAGR of 15.21% from 2024 to 2032. The growth will be fueled by factors including increased internet usage, ongoing digital transformation, rising cyber threats, regulatory compliance, heightened public awareness, adoption of advanced technologies, infrastructure modernisation, and international collaborations.
Addressing current and future challenges comprehensively will position Vietnam to harness the benefits of AI while mitigating potential risks, fostering economic growth, and improving the quality of life for its citizens.
Mohit explains that robust security measures not only protect sensitive information and prevent manipulation but also ensure the responsible development and long-term viability of AI, fostering confidence in its adoption across diverse applications and industries.
The country can benefit from AI adoption in several ways:
- Preserving Data Integrity and Confidentiality: AI can help protect sensitive information and ensure that data remains secure and private.
- Mitigating Manipulation and Exploitation Risks: By implementing robust security measures, AI systems can be protected against manipulation and exploitation by malicious actors.
- Maintaining AI Resilience: Ensuring that AI systems are resilient to cyber threats and can continue to function effectively even in the face of attacks.
- Building Trust in AI Technology: Building trust among users and stakeholders by demonstrating the security and reliability of AI systems.
- Ensuring Long-Term Viability: Implementing measures to ensure that AI systems remain viable and effective over the long term.
Through collaboration between entities, including government agencies, private sector organisations, and academia, Vietnam can leverage collective expertise and resources to bolster its cybersecurity defences. By enhancing digital infrastructure, such as upgrading network systems and deploying advanced cybersecurity technologies, the nation can create a more secure environment for AI adoption.
Additionally, promoting ethical AI practices ensures transparency and accountability, building trust among citizens and stakeholders and ultimately strengthening resilience against cyber threats.
Vietnam should focus on promoting responsible AI use by implementing ethical standards, ensuring transparency in algorithms, educating stakeholders on ethical implications, and establishing regulatory frameworks to build societal trust and acceptance.
“In navigating the intricate landscape of AI, securing its integrity and ensuring transparency isn’t just a matter of protection,” Mohit concludes. “It’s about safeguarding trust, ethics and the very fabric of our digital future.”
Welcome Address

Khang Nguyen Tuan, Security FLM Leader, ASEAN at IBM, delved into the complexities surrounding artificial intelligence (AI), providing a nuanced definition of Ethical AI as the development and deployment of AI systems that prioritise fairness, transparency, accountability, and respect for human values.
AI ethics revolves around comprehending the ramifications of AI on individuals, groups, and society as a whole, aiming to ensure safe and responsible AI utilisation, mitigate potential risks associated with AI, and prevent harm.
He underscores the critical importance of raising awareness about Ethical AI, particularly in light of AI’s pervasive integration across all sectors. This emphasis comes as the global AI market is projected to experience substantial growth, with an annual increase of 19.6%, reaching a staggering US$500 billion by 2023.
While AI and automation offer significant benefits such as increased efficiencies, greater innovation, personalised services, and reduced burden on human workers, they also present new risks and impacts that need to be addressed. This underscores the importance of prioritising Ethical AI principles in AI development and deployment.
The impact of AI in the insurance sector for instance, demonstrates how it can result in minority individuals receiving higher automotive insurance quotes and can ensure white patients are prioritised over sicker black patients for healthcare interventions. In law enforcement, algorithms used to predict recidivism can be biased against black defendants, assigning them higher risk scores than white counterparts even when controlling for factors like prior crimes, age, and gender.
To ensure Ethical AI, expertise in computer science, AI policy, and governance is essential, ensuring adherence to best practices and codes of conduct throughout system development and deployment. This multifaceted approach fosters a comprehensive understanding of ethical considerations, enabling the implementation of robust safeguards and mechanisms to uphold ethical principles in AI development and deployment.
“Taking proactive steps is crucial to managing unethical AI and staying ahead of upcoming regulations. Regardless of the stage of system development, measures can always be implemented to enhance the ethical standards of AI,” Khang says. “This is critical for companies to safeguard their reputation, assure compliance with evolving legislation, and deploy AI with increased confidence.”
Khang shares IBM’s proactive stance in promoting AI ethics and combating cyberattacks through AI technologies. IBM has developed a comprehensive framework for AI ethics, guiding data scientists and researchers to build AI systems that align with ethical principles and benefit society at large.
IBM’s Principles for Trust and Transparency serve as the cornerstone of their approach to AI ethics, influencing every aspect of AI development and deployment. These principles guarantee that IBM’s AI technologies are designed to enhance human intelligence, empowering individuals to achieve more while maintaining the highest standards of trustworthiness and transparency.
Moreover, IBM prioritises the active defence of AI-powered systems against adversarial attacks, aiming to minimise security risks and instil confidence in system outcomes. Khang emphasised IBM’s belief that AI should improve productivity and be accessible to all – not just a select few – underscoring the company’s commitment to democratising the benefits in the AI era.
“As we navigate the complexities of AI, expertise in computer science, AI policy, and governance becomes imperative to ensure adherence to best practices and codes of conduct throughout system development and deployment,” concludes Khang. “This approach not only safeguards against potential risks but also ensures the inclusive and fair deployment of technology.”
Technology Insight

Shaibal Saha, IBM’s Asia Pacific Digital Trust Leader, underscores the significance of AI in the Asia Pacific region, emphasising its increasing presence and potential impact across various industries and sectors.
“Similar to transformative technologies like steam engines, computers, and the Internet in history, digital technology has profoundly reshaped human society at an unprecedented pace and scale in the past two decades,” Shaibal says.” It has significantly bolstered socio-economic creativity and growth.”
Amidst these transformative opportunities, the Asia-Pacific region has stepped into the golden age of the digital economy, experiencing GDP growth rates surpassing 5% in numerous Asian countries in 2022. Notably, APAC has emerged as the fastest-growing AI market worldwide.
Excluding Japan, APAC’s investments in new technologies such as AI account for close to 40% of its total information communication technology (ICT) investments by the end of 2023. This growth trajectory is anticipated to continue for at least the next decade, far outpacing the rest of the world, which maintains a rough growth rate of 22%.
Despite the benefits of AI, significant concerns persist regarding the legal and ethical implications surrounding its implementation. Recent global data breaches have instilled widespread apprehension and reluctance towards data storage, deterring many potential users from venturing into unfamiliar technological landscapes. The challenges encountered in AI deployment and usage in APAC mirror those experienced worldwide.
“AI is useless without troves of data, but enterprises holding AI-processable data ought to ask a number of questions,” cautions Shaibal. “Given that most data used by AI is stored in the cloud, businesses must carefully consider their cloud storage provider’s security, support, and maintenance capabilities.”
Additionally, they should assess whether they are housing personal information, whether data has been de-identified or anonymised, and have robust data breach response plans in place. Alongside those considerations, businesses must address the ownership of such data and the data outputs containing proprietary rights.
Algorithms play a crucial role as the foundation of all systems, with many companies increasingly depending on them to make significant decisions. However, the potential for AI and algorithms to enhance business and social welfare also brings about material ethical risks.
Bias has been observed in the operations of some algorithms, prompting growing calls for a deeper understanding of their ethical implications. This includes advocating for transparency and providing more information regarding how these machines are trained and operate
However, current privacy laws often fail to satisfy companies seeking increased transparency or constraints on decision-making without human involvement. Nonetheless, some advocate for a “right to explanation”, allowing individuals to question automated decisions that impact them by understanding how algorithms operate.
Indeed, the aforementioned issues are just a few of the primary concerns identified by experts that require consideration by businesses and technology procurement teams. Given the rapid evolution of these legal areas, businesses may require assistance to stay abreast of local regulatory changes.
IBM is actively working to tackle these challenges by offering dependable and transparent AI solutions while advocating for compliance with relevant regulations. One crucial step in this process involves ensuring that companies’ AI systems can furnish sufficient explanations regarding decision-making processes, thereby empowering humans to comprehend and scrutinise automated decisions.
Additionally, IBM can assist in monitoring local regulatory changes related to technology, ensuring that companies remain compliant with applicable laws and can adapt their strategies accordingly.
“By providing ongoing updates and guidance on evolving regulatory landscapes, IBM helps organisations navigate complex legal frameworks while maintaining ethical and transparent AI practices, “ Shaibal concluded.
Closing Remarks
Khang expressed his appreciation for the enthusiasm and contributions of the participants at the OpenGov Asia Breakfast Insight. He believes that such opportunities provide a valuable platform for exchanging ideas and concepts concerning the security challenges in adopting artificial intelligence (AI).
Khang reiterated the importance of forming a clear vision for deploying AI to ensure that organisations safeguard their AI ecosystems while harnessing the transformative potential of this technology to the fullest extent.
The Vietnam Cybersecurity Market is forecasted to experience substantial growth with a CAGR of 16.8% by 2027. This growth is propelled by the increasing demand for digitalisation and scalable IT infrastructure. Notably, Vietnam achieved a commendable rank of 25th out of 194 countries in the Global Cybersecurity Index (GCI) in 2020, indicating a positive trajectory in cybersecurity efforts.
Vietnam, as a pivotal member of ASEAN, holds a significant position in advancing AI technology within the region. Despite rising cybersecurity concerns, the country has witnessed a decline in cyberattacks in recent years. However, challenges persist within the cybersecurity landscape.
Alongside the advancement of AI technology, there are many risks and challenges, including cyberattacks, such as phishing, data breaches, and others.
Conducting regular cyber risk assessments, ensuring system access is protected by strong passwords and multifactor authentication, and developing a cybersecurity strategy are all effective ways to keep criminals at bay.
“Every year, cybercriminals make millions of dollars by finding security vulnerabilities in computer systems to exploit or trick companies into giving them system access,” acknowledges Khang. “Firms can minimise cyberattack impact by regularly backing up their critical information and having a clear response plan in case of a security breach.”
Mohit concurs that companies must have a well-prepared response strategy in place. Such a strategy should entail identifying the individuals responsible for managing the situation, determining the sequence of informing relevant parties about the incident and specifying the appropriate response protocols. Immediate actions, such as changing passwords or isolating compromised equipment, may be imperative in certain cases.
Further, firms could opt to conduct business continuity exercises to ensure that their processes and procedures are not only in place but also strictly followed and well understood by all relevant parties. These exercises could involve practising switching to an alternative system and restoring data using online and offline backups.
“Establishing a clear response plan empowers firms to minimise the impact of cyberattacks and reduce company downtime,” Mohit concludes. “A proactive approach enables organisations to effectively mitigate potential damage and maintain operational continuity.