While forensic algorithms are tools used by law enforcement agencies to help determine whether an evidentiary sample, collected from a crime scene, is or is not associated with a potential source sample, collected directly from a person of interest, based on the presence of similar patterns, impressions, or other features in the sample and the source. Hence, forensic algorithms play a crucial role in modern criminal investigations, helping law enforcement determine whether an evidentiary sample can be matched to a specific person.
While technology can curtail subjective decisions and reduce the time it takes analysts to reach conclusions, it comes with its own set of challenges. According to a report on how forensic algorithms work, the Government Accountability Office (GAO) outlined the key challenges affecting the use of these algorithms and the associated social and ethical implications.
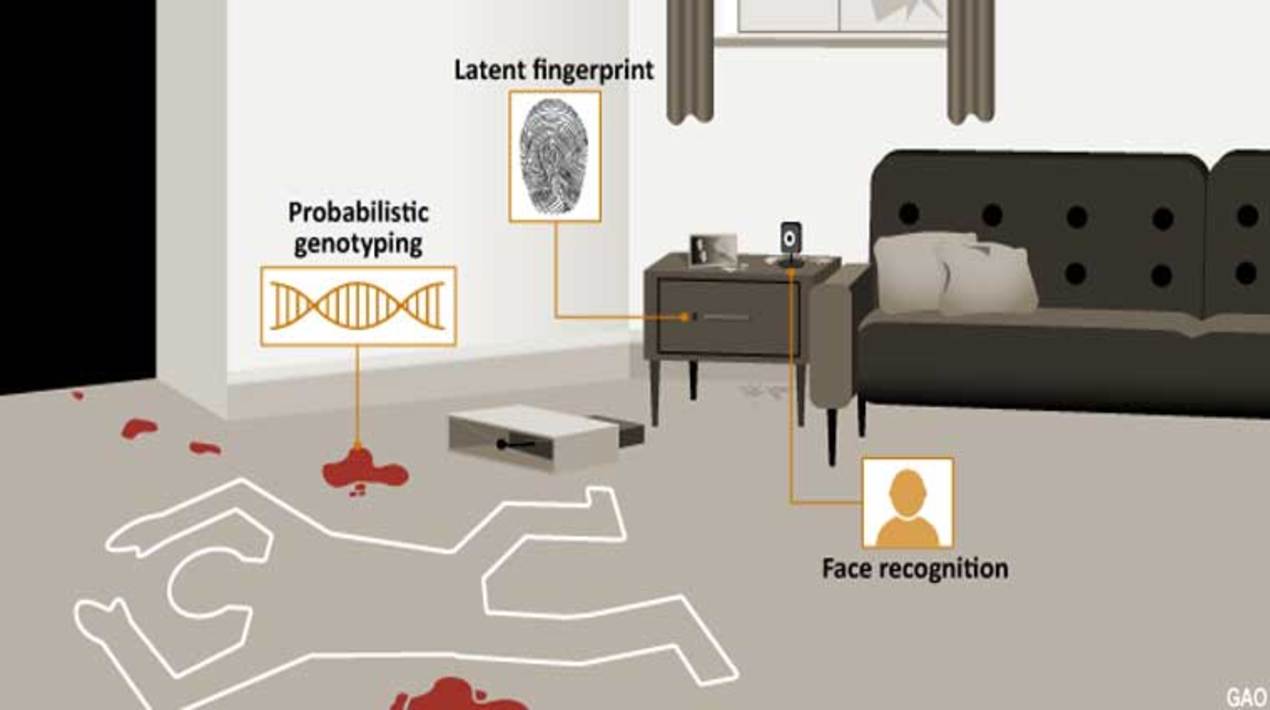
Federal law enforcement agencies primarily use three types of forensic algorithms to help determine whether an evidentiary sample is or is not associated with a potential source sample which includes latent prints, facial recognition and probabilistic genotyping.
All three compare evidence from crime scenes to an online database. However, several factors ranging from the quality of the evidence, the size of the respective database and age, sex and racial demographics have the potential to reduce the accuracy of these findings. Analysts themselves are subject to human error, and biases differ from person to person.
The accuracy of latent prints frequently relies on the percentage of the fingerprint covered in the sample and whether it is smeared or distorted, making it difficult to draw precise inferences when the quality of the evidence is compromised. Similarly, the accuracy of facial recognition algorithms can vary when individuals wear glasses or makeup or if the image was taken from an extreme angle.
Law enforcement also runs into problems assessing the validity of probabilistic genotyping, or the technology used in DNA profiling. Most studies evaluating probabilistic genotyping software have been conducted by law enforcement or software developers themselves. A report from the President’s Council of Advisors on Science and Technology noted that independent evaluation is often required to establish scientific validity, but there have been few such studies.
GAO offers policymakers three solutions to improve the reliability of forensic algorithms. The first involves increased training for law enforcement analysts and investigators to boost their understanding of the algorithms and the subsequent results. To reduce the risk of misuse and improve consistency, GAO says policymakers could also support the development and implementation of standards and policies related to law enforcement’s testing, procurement and use of such algorithms.
GAO also suggests that increased transparency related to testing and performance could improve the public’s knowledge of the technologies and help address corresponding challenges. By automating the assessment of evidence collected in criminal investigations, forensic algorithms can expand the capabilities of law enforcement and improve objectivity in investigations. However, use of these algorithms also poses challenges if the status quo continues.
U.S. researchers have been utilising an algorithm to solve many problems in different fields, including face recognition algorithms for flight boarding. As reported by OpenGov Asia, The most accurate face recognition algorithms have demonstrated the capability to confirm airline passenger identities while making very few errors, according to recent tests of the software conducted at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST). The findings focus on face recognition (FR) algorithms’ performance under a particular set of simulated circumstances: matching images of travellers to previously obtained photos of those travellers stored in a database.
This use of FR is currently part of the onboarding process for international flights, both to confirm a passenger’s identity for the airline’s flight roster and also to record the passenger’s official immigration exit from the United States. The results indicate that several of the FR algorithms NIST tested could perform the task using a single scan of a passenger’s face with 99.5% accuracy or better — especially if the database contains several images of the passenger.
















