In today’s dynamic business landscape, companies need to adapt to changing market conditions, evolving consumer expectations, and technological advancements to remain competitive and successful.
Cloud computing and modern applications provide organisations with on-demand access to computing resources, data, and applications, empowering them to utilise these resources whenever required.
An organisation’s IT infrastructure acts as the backbone, providing the necessary computational power and storage to execute programmes and store data effectively.
The availability of adaptable, secure and scalable design options for modern IT infrastructure empowers businesses to respond to shifting demands and requirements effectively. Currently, organisations have the flexibility to host their infrastructure on-site, in the cloud, or adopt a hybrid approach combining both options to meet their specific needs and preferences.
Citizen participation is a vital element of digital transformation, enabling governments and organisations to engage with constituents and better understand their needs to deliver improved services and outcomes.
Digital tools such as social media, smartphone apps and chatbots provide effective means to engage citizens, offering relevant information and services while facilitating convenient and interactive communication channels.
In today’s rapidly evolving business world, agility is essential. Businesses must be able to react swiftly to shifting consumer demands, shifting market conditions and new technological developments. This calls for a culture of creativity, cooperation, and ongoing improvement in addition to the ability to quickly adopt new technology.
In the era of digital transformation, ensuring security is paramount to protect sensitive data from unauthorised access, theft, or loss. With the exponential growth in data generation and processing, robust security measures are essential to mitigate risks and safeguard valuable information.
To ensure the confidentiality, integrity and availability of data and applications, businesses need robust security policies and technologies that provide strong protection against threats and vulnerabilities. Implementing effective security measures is crucial in safeguarding valuable assets and maintaining the trust of customers and stakeholders.
These are all essential components of a successful digital transformation because they help organisations become more adaptable, creative and responsive to the needs of their stakeholders and customers.
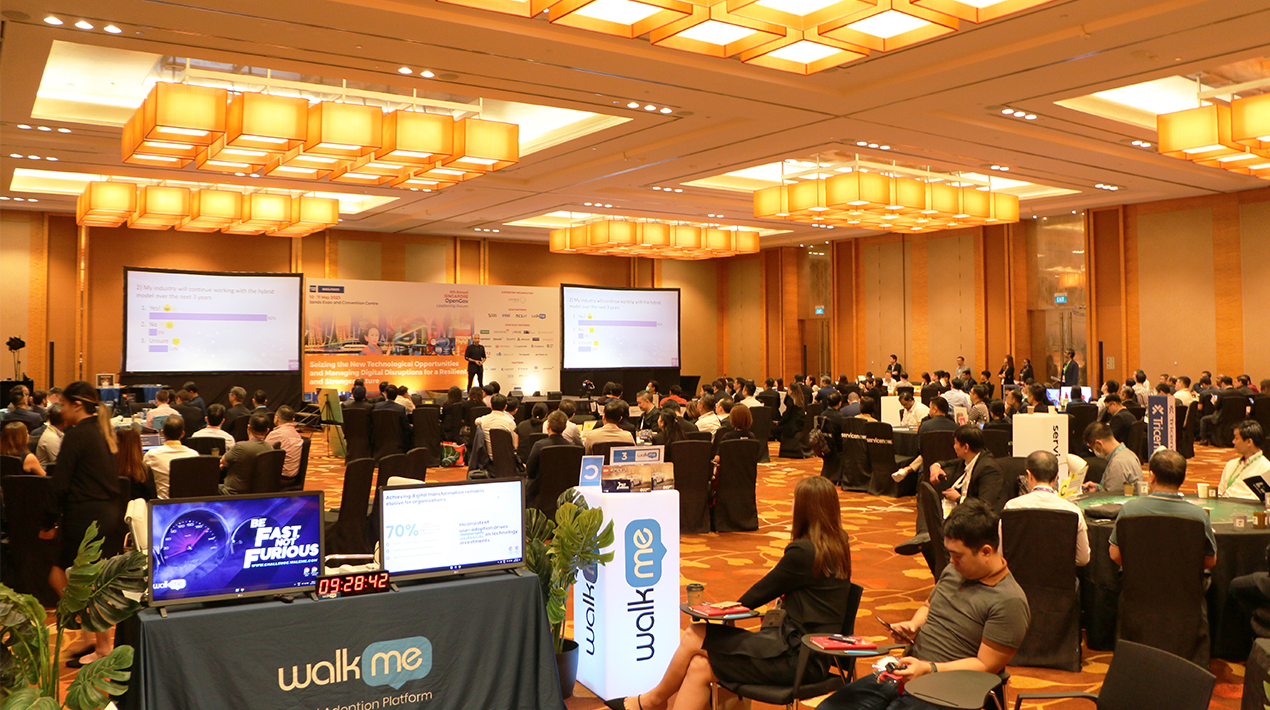
On the first day of the 8th Annual Singapore OpenGov Leadership Forum 2023 held on 10-11 May 2023 at Sands Expo and Convention Centre, Singapore, technology leaders tackled the Cloud, IT Infrastructure, Modern Applications, Citizen Engagement, Agility, Security, Productivity and Operational Transformation that will help boost the efficiency of the different sectors.
Opening Remarks

Mohit Sagar, the CEO and Editor-in-Chief of OpenGov Asia, acknowledges the importance of leveraging technology to enhance the lives of citizens but emphasises the need for efficient, reliable, and secure IT systems.
He further observes a change in the priorities of organisations seeking CIOs in recent times. “Companies are currently seeking IT leaders who can effectively deliver fundamental aspects like uptime, security, and cost optimisation, rather than focusing solely on innovators who can push the envelope and are capable of driving significant change.”
There has been a significant disparity in investment allocation between customer-facing services and products, which receive substantial funding for innovation, and middle and back-office core system updates, which receive comparatively fewer financial resources.
This lopsided approach can often lead to a situation where organisations prioritise new customer experiences and neglect the necessary updates and improvements to their internal systems. There is a growing need to address this gap and allocate adequate funding and attention to ensure the reliability, efficiency and modernisation of core systems that support the overall business operations.
This new paradigm can be attributed to tighter budgets, reduced risk appetite, and the realisation that organisations may have neglected to keep an eye on their foundational IT investments. As a result, there is a greater emphasis on effective continuity rather than pursuing extravagant innovations.
Organisations must find a balance between keeping the lights on and investing in new solutions to address evolving business needs. No doubt they should allocate resources towards innovation and development to stay competitive and meet future challenges effectively but first must ensure operational stability and efficiency and maintain the smooth functioning of current infrastructure.
Mohit cited the case of an airline that experienced a major breakdown in their crew-scheduling technology, resulting in the stranding of thousands of passengers during a peak travel period. This incident served as a clear example of the consequences that can arise from a lack of investment in fundamental infrastructure.
It underscores the importance of allocating resources to maintain and enhance the core technological foundations that support efficient operations and customer satisfaction.
“Recent market developments have raised awareness of the importance of fundamentals that may have been disregarded in the past,” says Mohit. “This is because there is less opportunity for failure in a tighter economy. It may be necessary to readjust the focus towards prioritising the reliability and currency of core operations and underlying digital investments.”
Nations are facing similar challenges as they make substantial investments in areas such as education, healthcare, sustainability, and transportation.
While these areas are critical for improving citizens’ lives, governments should not overlook the importance of solid IT strategy and maintaining the underlying foundational systems. Without these core mechanisms, the idea of a truly smart nation may not be realised.
“The country must balance its priorities between continuity and innovation to ensure the success of its smart nation vision,” Mohit concludes.
Technology Case Study: Analytics Everywhere, For Everyone: Democratising and Simplifying AI and Machine Learning Into Actionable Insights Through a Reimagined Cloud-native Architecture

According to Jason Loh, Head of Technology Futures at SAS, the growing utilisation of online services by citizens and customers, coupled with the accelerated adoption of digital transformation by enterprises, has given rise to new goals and expectations. This shift necessitates organisations to adapt and meet the evolving needs of their digital-savvy stakeholders.
By leveraging an analytics platform that supports a low-code/no-code approach, organisations can involve a broader range of individuals, foster ongoing innovation and accelerate digital transformation. As analytics and machine learning gain prominence, such a platform facilitates the adoption and implementation of these technologies across the entire company.
SAS, a leading provider of analytics and business intelligence software, attributes its success to key factors such as a comprehensive product portfolio, expertise in advanced analytics, and a robust network of strategic partners. These attributes contribute to SAS’s position as a trusted and influential player in the industry.
“One of SAS’s significant advantages is its long-standing market presence and trusted brand, which has earned the company much customer respect,” reveals Jason. “SAS is chosen by businesses due to its enterprise-grade platform capabilities and comprehensive analytics life cycle support.”
SAS sets itself apart with its Viya platform, empowering clients to scale and operationalise AI pipelines while integrating analytics directly into decision-making processes. This capability enhances the effectiveness and efficiency of organisations in leveraging data-driven insights.
The platform enables efficient analysis and identification of fraudulent activities, resulting in significant cost savings for these budget-intensive portfolios. In areas of government oversight, it can be difficult to quantify the return on investment for improved audits, inceptions and investigations.
Government agencies leveraging SAS Viya for investigations across various mandates, such as health, tax, and social benefit programmes, can easily quantify the financial gains achieved through fraud detection and prevention, minimising waste and misuse of funds.
A concrete example is SAS and the US FDA establishing a partnership that goes beyond the foundational or submission environment. They are utilising the advanced capabilities of SAS Viya for three innovative use cases: Adverse Event (AE) Reporting, Manufacturing Site Surveillance and Drug Repurposing. These initiatives are driving the digital transformation at the FDA, enhancing their processes and enabling more efficient and effective operations in these critical areas.
This significant investment from US FDA demonstrates the continued trust in SAS not only today but also for the future to come.
Technology Case Study: Journey to Intelligent Data Management for the Multi-Cloud World

Raymond Goh, Vice President of Sales Engineering, APJ, Veeam recognises that data availability and resiliency have reached new levels of expectation in the current data-driven world. As organisations heavily rely on data, ensuring its accessibility and resilience has become increasingly crucial for meeting the demands of today’s business landscape.
“Data must move to a new state of intelligence, able to automatically anticipate threats, needs and meet demand. Data must securely move across multi-cloud infrastructures,” he is convinced.
Moreover, data must meet the expectations of the mobile and always-on world. Intelligent Data Management brings new insights from data and rapid productivity increases to speed the pace of innovation and delivery of new digital services and experiences that improve how people live and work.
Raymond shared the 5 Stages of Intelligent Data Management:
Protection: Protect all workloads using backups, complemented by snapshots and replication where appropriate, to ensure they are always recoverable and available in the event of outages, cyber threats, accidental loss or theft.
Mobility: Provides easy portability and fast recovery of ANY on-premises or cloud-based workloads to maintain Business Continuity and Availability across hybrid cloud environments.
Observability: View the full breadth of your data, accompanied by the infrastructure that it passes through and resides on so that you can pivot from reactive to proactive management for better business decisions including proactive measures to defend against cyber threats.
- Orchestration: Optimise data utilisation across multi-cloud environments with workflows that ensure consistent execution of otherwise manual and complex backup, recovery, and data management tasks.
- Automation: Data becomes self-managing by learning to protect itself with appropriate SLAs, methods, locations and cyberthreat-aware to meet business objectives or comply with broader IT initiatives.
The Data Domain Group, encompassing data governance, architecture, protection, sharing and storage, aims to ensure that agencies put in place effective data management practices to utilise and safeguard data in all stages of its lifecycle.
This sets out the requirements for the access and distribution, and exploitation of data, which is necessary for sharing of data, organised into the following domains: Data Classification, Data Protection (Data Security), Data Acquisition, Data Processing and Fusion, and Data Access and Distribution.
Recovering from ransomware can be a messy process and most solutions aren’t designed to provide recovery at the scale created by ransomware.
“At Veeam, we know every environment is different and you need a solution that allows you to recover your data. That’s why we’re talking after all. And that’s really what makes us different – choice,” Raymond concludes.
Technology Case Study: Why Zero Trust CDR is the Only Way Forward?

Daniel Turner, VP and General Manager, Deep Secure Business Unit, Forcepoint, emphasises that in today’s digital age, organisations rely heavily on digital content to communicate, work together and share information.
Digital information encompasses a wide range of electronic data, including files, documents, images, videos, music, and more. It refers to any data that is utilised, transmitted or stored in digital form. Regrettably, cybercriminals can exploit digital information to gain unauthorised access to systems and data, causing harm and potential damage, Daniel explains.
One of the most advanced and targeted kinds of cyberattacks is called a “zero-day” cyberattack. These intrusions represent highly sophisticated and targeted methods that exploit undiscovered vulnerabilities in software, apps, or systems, exploiting them before any patch or fix can be developed and deployed.
These insidious attacks pose significant challenges as they often conceal themselves within everyday digital files, documents, and images that are commonly found within an organisation’s systems, making them difficult to detect and defend against.
Normal measures do not contain or thwart such attacks. Firewalls, antivirus software and intrusion detection systems, for example, are not always effective against zero-day cyberattacks. They rely on known threats and signatures, which zero-day assaults lack. This means that organisations must take a more proactive and comprehensive approach to cybersecurity.
“Adopting a zero-trust security model, which implies that all content is potentially hazardous and cannot be trusted, is one answer,” Daniel believes. “This method entails validating every person, device and application that connects to the organisation’s systems and data.”
Advanced threat detection and response systems that use machine learning and artificial intelligence to detect and respond to zero-day assaults can also be deployed by organisations.
Forcepoint ONE, an all-in-one cloud platform, is designed to safeguard a hybrid workforce’s access to information on the web, in the cloud and in private applications.
“Unlike other cloud-based security solutions that combine disparate product portfolios, we designed Forcepoint ONE to integrate Zero Trust and Security Service Edge (SSE) technologies into a single cloud platform,” Daniel explains. “This integration allows organisations to manage a single set of policies in a single console connected to a single endpoint agent.”
The fact is that digital content is critical to any organisation’s success, but it can also be the chosen carrier for today’s sophisticated zero-day cyberattacks, Daniel reiterates. Traditional detection-based defences are no longer sufficient to protect organisations against these threats.
To proactively protect against these threats, organisations should implement a zero-trust security strategy as well as advanced threat detection and response solutions, like Forcepoint ONE.
In Conversation With: The Evolving Role of Data Sovereignty: Transforming Compliance to a Key Market Driver
Data sovereignty implies that data is subject to the laws and regulations of the country where it resides, ensuring compliance with local governance and data protection policies. With the continuous growth of data generation and retention, data sovereignty has emerged as a critically important concern for multinational organizations.
The growing importance of data sovereignty is transforming compliance from being solely a regulatory burden to becoming a significant driving force for businesses. Organisations that can negotiate the complicated terrain of data sovereignty legislation and demonstrate a commitment to data privacy and compliance will do well in today’s global marketplace.

Kenny Seah, Head of IAM & Security Consulting at Adnovum Singapore, emphasises the importance for organisations to have a clear understanding of their technology requirements. This ensures that technology investments align with business goals, enhance efficiency and productivity, reduce costs, foster innovation and competitiveness, manage risks effectively, enable scalable growth and meet stakeholder expectations.
“By figuring out what they need, organisations can make smart choices, choose the right technologies, and use technology as a strategic tool to help them succeed,” Kenny explains.
While security controls may vary between on-premises and cloud environments, it is essential to recognise that the core objectives and principles remain unchanged. Regardless of the setting, the primary goals are to safeguard data, systems and infrastructure against security risks.
He is of the view that organisations should assess their unique security requirements, consider the shared responsibility model in the cloud (where the cloud provider and the organisation have distinct security responsibilities) and implement appropriate security controls. This approach helps mitigate risks and ensures a secure computing environment, irrespective of the chosen deployment model.
“Cybersecurity is an important part of how an organisation runs, and it can’t be given to just anyone,” says Kenny.”It’s important to think carefully about and choose trusted partners or service providers who have the knowledge and skills to deal with cybersecurity issues.”
Even though outsourcing cybersecurity can bring benefits like access to specialised knowledge and lower costs, organisations should still keep a close eye on what’s going on and make sure they maintain a strong company cybersecurity posture.
Setting up clear contracts, checking the provider’s performance regularly and retaining a strong internal security programme will help make sure that cybersecurity is a top priority for organisations.
Data protection and privacy have become significant concerns for organisations across industries in today’s digital landscape. As customers and stakeholders become increasingly aware of the value of their personal data, they are seeking reassurance that organisations are taking the necessary precautions to protect and safeguard it.
Consequently, businesses recognise the importance of differentiating themselves by demonstrating a strong commitment to data security and privacy.
Organisations can demonstrate their commitment to data protection and privacy through various means, including the implementation of robust security measures, adherence to privacy-by-design principles, regular audits and risk assessments, transparent data handling practices, and effective communication of privacy policies to stakeholders.
These actions collectively demonstrate a strong commitment to safeguarding data and respecting privacy concerns. They not only assist organisations in meeting legal requirements but build a culture of trust and accountability in data handling, distinguishing them from competitors.
Deploying a multi-layered security strategy is critical for organisations to safeguard their data from unauthorised access, and breaches, and to maintain regulatory compliance. Strong Identity and Access Management (IAM), Encryption, Access Controls, Compliance and Governance, Security Monitoring and Incident Response, and Employee Awareness and Training are some essential security techniques and procedures that organisations can implement.
Security is a continuous process, and organisations must constantly assess and improve their security procedures to handle evolving threats and weaknesses. Collaboration with security professionals and maintaining current industry best practices can assist organisations in staying ahead of potential security problems and protecting their important data assets.
Organisations can use tools and techniques such as Data Classification and Policy Enforcement, Monitoring and Auditing Tools, Access Control and Privilege Management to create a balance between data protection and accessibility.

Melvin Koh, Head of Sales Engineering, ASEAN Thales reiterates that classifying data is important for data organisation, security, compliance, control, analysis, allocating resources, and collaboration.
“Classification offers a structured approach to managing data, enabling organisations to leverage its value while ensuring proper protection and appropriate usage,” he notes.
To keep data safe in on-premise and multi-cloud settings, organisations need to take both technical and organisational steps. Data Classification, Encryption, Access Controls, Data Loss Prevention (DLP), Data Governance and Policies, Backup and Disaster Recovery and other measures are all important to consider.
“Remember that protecting data is a process that never ends,” Melvin warns. “Review and change your security methods often so you can keep up with new threats and technologies. Stay up to date on the latest best practices and security frameworks to protect your data in both on-premise and multi-cloud settings.”
From his perspective, centralised solutions for data security involve the management and protection of an organisation’s data through a single platform or system. This approach ensures a consolidated and secure environment for data management.
These systems offer a unified way to protect data, making it possible to control, monitor and enforce security measures from one place.
When adopting centralised solutions, it’s important to make sure they meet the security needs, compliance standards and data protection policies of the organisation. They must take into consideration issues like scalability, integration and vendor support.
“Regular monitoring, updates, and audits are needed to make sure these methods work and to deal with new security issues as they come up,” Melvin points out. “It’s important to remember that having encryption keys in a safe place comes with responsibilities.”
Maintaining a secure data environment requires regular monitoring, auditing and ongoing enhancement of security procedures. It is critical to tailor the approach to each organisation’s unique demands and regulatory constraints.
In addition, organisations must strike a balance between data security and accessibility by utilising appropriate technologies and strategies.
By leveraging cutting-edge technologies, agencies and organisations have the opportunity to establish robust data sovereignty rules that prioritise the security and privacy of their data. This proactive approach helps build trust and confidence among individuals and consumers, demonstrating a commitment to protecting their sensitive information.
Some effective strategies for ensuring data security include implementing strong encryption techniques, adopting privacy-enhancing technologies, conducting regular audits and compliance assessments, seeking independent audits and certifications, implementing proactive data security measures, and embracing a zero-trust architecture. These measures collectively contribute to safeguarding data and maintaining a robust security posture.
Agencies and organisations can demonstrate their commitment to data sovereignty, security, and privacy by deploying these cutting-edge technologies and tactics. This, in turn, contributes to the development of trust among people and customers, establishing better relationships and encouraging the proper use of data.
Power Talk: Are You a Future-Ready Organisation?: Modernising Digital Infrastructure for Agility, Security, Scalability and Sustainability
Modernising digital infrastructure can ultimately assist organisations in remaining competitive, enhancing efficiency, minimising risk and promoting sustainability and responsible resource management.
To upgrade digital infrastructure, organisations must take a comprehensive approach that includes evaluating their current infrastructure, identifying areas for development and implementing a modernisation road map. This could entail investing in new technologies, migrating to the cloud and/or implementing new development methodologies and security procedures.

For Arjun Chib, Managing Director of Standard Chartered Bank, it’s critical to understand the organisation’s objectives, evaluate its needs, and, most difficult of all, come up with viable options. Solutions must be quick to implement, secure, scalable and cost-effective.
Integrating data can pose challenges for organisations due to its inherent complexity. It requires consolidating data from multiple sources, ensuring consistent formatting, and conducting thorough checks for quality and reliability.
To effectively manage and minimise the impact of security incidents, organisations must promptly address issues such as breaches, Arjun explained. Additionally, data backups play a crucial role in enabling efficient incident response and facilitating recovery processes.
Achieving harmony and synergy between social progress, environmental preservation, sustainability and economic growth is essential. This equilibrium is a crucial component of making ethical decisions and helps to create a future that is sustainable for both people and the environment.
“Organisations must prioritise minimising their environmental impact, conserving resources and actively contributing to a more sustainable future by modernising digital infrastructure,” Arjun furthers. “Adopting sustainable practices can also result in financial savings, increased operational effectiveness, and improved reputation.”
Banks have the opportunity to capitalise on the growing market demand for sustainable goods and services by integrating sustainability into their business plans and product offerings. They can enhance their long-term financial viability through the creation of new revenue streams while simultaneously fostering positive environmental and social impacts.
By aligning their operations with sustainable practices, banks can attract environmentally conscious customers, meet regulatory requirements and contribute to the development of a greener economy. This strategic approach not only benefits the environment but also enhances the bank’s reputation and strengthens its position in a market that increasingly values sustainability.
On the other hand, public-private partnerships (PPPs) provide a collaborative framework that leverages the skills and resources of both the public and private sectors to drive infrastructure modernisation efforts forward. By joining forces, these partnerships maximise the potential for success and effectively utilise the collective expertise and assets of each sector.
“PPPs can provide durable and significant infrastructure projects that benefit societies and contribute to economic development by combining public sector oversight, policy frameworks, and accountability with private sector efficiency, innovation, and investment,” Arjun believes.
Hwai Siang Khor, Senior Director Solutions Engineering at NCS, recognises the long-standing reliability and functionality of certain well-established systems that have served organisations effectively over many years of operation.
“Some legacy systems have been running for many years and may well need upgrading. However, I believe the most important thing is to determine what kind of goals you want to achieve while trying to modernise your applications.”
It is essential for organisations to clearly define their key objectives for cloud adoption and align them with their overall business strategy. This will guide the cloud adoption process, including selecting the appropriate cloud service model and the right cloud provider that best meets their specific needs and objectives.
“Most of the time, when we engage with a client, the first question we ask is whether or not they have a holistic data security and governance framework, as this underpins how they execute the plan in terms of securing their cloud or on-premises industry infrastructure and how they will mitigate in the event of an incident,” Hwai Siang elaborates.
Hwai Siang consistently advises clients to prioritise evaluating their data security framework, including data encryption methods and handling protocols for different data classifications, before delving into solution implementation.
Organisations need to consider the sustainability implications of AI adoption and ensure that AI solutions align with their sustainability goals. This includes assessing the environmental impact of AI infrastructure, considering the social consequences of AI-driven decisions and promoting ethical AI practices.
By intentionally integrating sustainability into AI initiatives, organisations can leverage the power of AI while minimising negative environmental and social effects, ultimately driving positive change and contributing to a more sustainable future.
Hwai Siang acknowledges that cloud providers have made commendable progress in effectively managing the carbon footprint within their data centres. Through proactive management, cloud providers make a meaningful contribution to global sustainability endeavours while offering businesses and organisations environmentally responsible solutions.
He believes it is important for organisations to assess their specific needs, consider the benefits and potential challenges of cloud adoption and evaluate the suitability of cloud services for their particular use cases.
The adoption of cloud computing brings notable benefits in terms of scalability, cost efficiency, agility, reliability and security. However, to ensure successful implementation, careful planning and consideration of factors such as data privacy, vendor lock-in, and integration requirements are of utmost importance.

Joseph Yang, Managing Director, Hewlett Packard Enterprise, Singapore feels that it is important for organisations to assess their current IT landscape, identify areas that need modernisation, and develop a strategic implementation plan.
Modernisation should be driven by specific business objectives and aligned with overall organisational goals. It requires careful planning, resource allocation and collaboration between IT teams and business stakeholders to ensure successful adoption and achieve the desired outcomes.
“We need to know the value of any change we make, whether it’s increased speed, better security or greater adaptability,” Joseph says emphatically.
While there are differences between academic and enterprise computing, there are also areas of overlap, such as the use of cloud computing, data analytics and security practices. Both domains can learn from each other and adopt best practices to improve their computing environments and achieve their respective objectives.
“Maintaining control over the security of academic materials to prevent unauthorised leaks, while simultaneously providing researchers and students with necessary access, is of utmost importance.” Joseph elaborates. “Balancing these requirements within the dynamic framework of cloud technology introduces intriguing challenges.”
He agrees sustainability is a fundamental component of accountable corporate and personal behaviour, encompassing environmental stewardship, social responsibility, and economic viability. It plays a crucial role in addressing the pressing challenges facing the planet and ensuring a sustainable future for generations to come.
“By embracing technological sustainability, organisations can contribute to a more sustainable and equitable future while reaping the benefits of efficient and responsible technology usage,” Joseph concludes.
Technology Case Study: Staying Competitive in the Digital Age: Leveraging Observability and AIOps for Better IT Resilience

Taylor Chan, as the Head of Sales Engineering at SolarWinds in South East Asia, understands the importance of resilient IT infrastructure in the modern digital era.
Cutting-edge technology comes with a plethora of advantages but is accompanied by a host of inherent dangers.
Generative AI has grown in prominence in recent years due to its capacity to produce realistic and high-quality content that is difficult to tell apart from human-generated content. It can create novel and distinctive data, such as photographs, videos, and text, that closely resemble existing data.
“As businesses adopt advanced, complex technologies to remain competitive and relevant in the current digital era, it can be difficult to obtain insights and effectively manage the resulting complexity,” Taylor believes.
Organisations must possess the ability to swiftly adjust their IT systems to meet evolving business requirements and customer expectations to retain their competitive edge.
Observability and AIOps are two key technologies that can help organisations attain greater IT resilience.
According to Taylor, these technologies can help organisations improve their IT operations and strength. IT AIOps refers to the use of software to automate and improve IT operations using analytics and machine learning (ML).
AIOps are commonly employed to optimise operations and gain valuable insights into performance. End-user experience management, proactive, predictive performance, trend analysis and root cause analysis are all common use cases for AIOps and observability.
Observability brings several key additional benefits including the detection of the root cause of problems and providing a clear understanding of their impact on the system or service. It helps in efficiently resolving identified issues and implementing appropriate remedies.
Observability promotes transparency by providing visibility into the inner workings of the service or system. It also extends its reach beyond the boundaries of the service or system, offering visibility into interconnected components and dependencies and facilitating a holistic understanding of the ecosystem.
Taylor defines business transformation as the process of driving significant change in an organisation’s operations, culture and customer experience via the use of technology, innovation and new ways of working.
Change has advantages but can challenge operational resiliency, the ability to endure and recover from unexpected disruptions in operations. Careful planning and mitigation strategies are crucial to maintaining resilience during transitions.
Taylor highlighted several instances where business transformation acceleration poses challenges to operational resiliency:
- Complexity, security and productivity challenges
- Issues with remote work – which is likely to remain in some shape
- IT budgets and resource constraints
- Modernisation of operations, apps and databases
- Multi-cloud deployments
- Flexible consumption models
To sustain good operational resiliency, organisations must develop from monitoring to observability to autonomous operations.
The SolarWinds Platform is a great solution. It is meant to interface with important business services and provide flexibility, visibility, and control – anywhere the environment is and wherever it is going. It offers simplicity, with deployment strategies that support clients today and tomorrow, on-premises and cloud-native SaaS solutions, Taylor concludes.
Technology Case Study: Building and Securing Modern Applications Consistently Across Hybrid Cloud

According to Kelvin Loh, Senior Manager, Solution Architecture, ASEAN, Red Hat, numerous organisations are delving into hybrid and multi-cloud architectures as they embark on their application modernisation endeavours.
Nonetheless, organisations have expressed concerns regarding several key aspects, including security and compliance, data sovereignty, as well as the scarcity of cloud-based skills and platforms across multiple environments.
Against this backdrop, aligning processes and resources through the adoption of Automation and GitOps best practices can enable companies to achieve a secure zero-trust Software Supply Chain. By embracing infrastructure and policies as code, they can effectively meet regulatory requirements while ensuring a robust and secure environment.
Sovereign Cloud offers the ability to exercise control over the location, access and processing of data within a cloud environment, addressing emerging industry standards and compliance requirements specific to certain nations or industries. This approach empowers organisations to maintain sovereignty over their data while adhering to relevant regulations and industry guidelines.
Red Hat® Advanced Cluster Management for Kubernetes offers centralised management for clusters and applications through a single console, while also integrating security policies. This solution from Red Hat ensures compliance, monitors resource utilisation and maintains uniformity across the environment.
With Advanced Cluster Management, organisations can effectively manage their Kubernetes infrastructure, enhance security measures, achieve regulatory compliance and ensure consistent operational efficiency.
“Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management for Kubernetes is bundled with Red Hat OpenShift Platform Plus, a comprehensive suite of optimised, potent tools for securing, protecting, and managing the applications,” Kelvin explains.
GitOps is a practice that leverages Git repositories as the authoritative source of truth for delivering infrastructure as code. It provides a standardised methodology for application development, offering several benefits to organisations.
It enhances security by enabling the definition of application requirements in advance, ensuring that security measures are integrated into the development process from the start. GitOps improves reliability by providing visibility and version control through Git repositories.
Additionally, it ensures consistency across various environments, whether it’s any cluster, any cloud, or any on-premises setup.
On the other hand, the Policy-as-Code enables teams to automate the policy decision-making process by codifying them using declarative language. When deployed, the tool will continuously monitor and simulates the policy-checking decisions that previously would have required manual checks.
According to Kelvin, managing and securing the cloud can be simplified through the following:
- Manageable at scale across multiple clouds. It enables the organisation to define the locality of their applications and data based on the security classification or even consumption cost;
- Codification ensures consistency and repeatability. It enables security at runtime and reduces manual checks and avoids human errors
- Establishing a delivery pipeline with inherent security capabilities and guardrails while automating the delivery of applications.
“These will result in reducing cost, increasing security, increasing efficiency and increasing predictability,” says Kelvin. He added that building and securing modern applications consistently across hybrid cloud environments is important as it allows organisations to take advantage of the benefits of cloud computing while minimising risk and maximising value.
Fireside Chat: Empowering Citizen-led Innovation: Maximising Citizen Experience with Low-Code Development Tools

Raymond Wong, the Singapore Country Manager, ServiceNow, describes low-code development tools as software platforms that empower users to build applications with minimal coding or development expertise.
These platforms can be used to rapidly develop and deploy custom applications, helping organisations to improve their digital capabilities and deliver better services to citizens.
“Low-code development tools can help organisations to maximise citizen experience by enabling rapid application development, customisation, integration, agility and cost-effectiveness,” Raymond emphasises. “By leveraging these tools, organisations can improve their digital capabilities and deliver better services to citizens, while also reducing the cost and complexity of development.”
Low-code development tools have indeed emerged as a powerful solution to address challenges and empower non-technical users, often referred to as citizen developers, to create applications quickly and easily. These tools allow citizen developers to contribute to the application development process. This democratisation of app development enables faster innovation, reduces the IT backlog, fosters collaboration, and empowers business users to create applications aligned with their specific needs.
However, it is important to establish appropriate governance and oversight to ensure the quality, scalability, and security of applications developed using low-code platforms.
Raymond also highlights the significance of citizen development, which involves the creation of software applications or solutions by non-professional developers. This process allows individuals without extensive programming experience to contribute to software development initiatives.
Low-code development tools empower non-technical users to create or modify applications according to their specific needs, enhancing business processes without the need for extensive coding knowledge or expertise. This enables individuals to customise applications and streamline workflows in a user-friendly and efficient manner.
Software development has traditionally been the purview of professional programmers and IT divisions. Citizen development, on the other hand, leverages low-code or no-code platforms and tools to enable users with limited computing skills to build applications via visual interfaces, drag-and-drop components, and pre-built templates.
Citizen development requires platforms to execute their jobs – systems that allow them to standardise everything from management to reporting.
Citizen development offers several benefits:
- Empowerment: It allows non-technical users to take control of their software needs and create solutions independently, reducing reliance on IT departments and enabling faster response to changing requirements.
- Agility: Citizen developers can quickly prototype and iterate on applications, accelerating the development process and facilitating rapid innovation.
- Cost savings: By eliminating the need for dedicated development resources, citizen development can reduce costs associated with outsourcing or hiring professional developers.
- Increased productivity: Non-technical users can build applications tailored to their specific needs, improving efficiency and productivity within their teams or organisations.
- Collaboration: Citizen development often encourages collaboration between business users and IT professionals, fostering better communication and understanding of requirements.
However, citizen development requires certain considerations:
- Governance and control: It’s important to establish governance frameworks and guidelines to ensure the security, quality, and compliance of citizen-developed applications.
- Training and support: Providing adequate training and support is essential to help citizen developers understand the tools, best practices, and potential limitations.
- Integration and scalability: Citizen-developed applications may need to integrate with existing systems or scale to accommodate growing demands, requiring technical expertise or collaboration with IT teams.
- Maintenance and updates: Ongoing maintenance and updates of citizen-developed applications need to be considered to ensure their longevity and compatibility with evolving technologies.
Citizen development democratises the software development process by permitting a broader range of individuals to contribute to application creation and customisation, resulting in increased organisational agility, productivity and innovation.
Raymond suggests the establishment of a Centre of Excellence (CoE) as an initiative to promote a shared understanding of objectives and desired outcomes within an organization. With a focus on agility and adaptability, a CoE cultivates a culture that is responsive and flexible in the face of changing market or environmental conditions. This enables the organisation to proactively adapt and stay competitive in dynamic landscapes.
“CoE provides techniques to ensure that everyone understands what citizen development entails and what they expect to accomplish, also known as agility or the capacity to adapt,” Ramond elaborates. “Before defining the policies, specify the expected boundary and explain the innovation explicitly.”
A shortage of technical resources and talent, he continued, is one of the most significant obstacles to accelerating digital transformation. In many organisations, the demand for competent IT professionals exceeds the available supply, resulting in a talent gap.
By automating processes and streamlining interactions with citizens, businesses can improve the overall citizen experience, reduce manual effort, increase efficiency, and provide citizens with quicker and more accurate services.
“Fostering a culture of innovation that embraces both technological and non-technical aspects can drive positive change within an organization,” Raymond concludes.
Technology Case Study: Preventing Your Organisation From Becoming a Breach Statistic

Adam Biviano, Director, Sales Engineering APAC, ForgeRock believes that implementing Open Finance services is a good solution for financial organisations looking to expand their business.
Open Finance is the next step in the growth of open banking. If Open Banking allows customers access to bank transaction data on various products and services, Open Finance offers customers access to broader data that may be used to personalise financial solutions.
“To guarantee this, it is imperative to have a well-prepared Digital Identity solution in place as a crucial supporting element within the Open Finance ecosystem,” Adam elaborates. “In the face of severe personal data protection rules in numerous nations and growing cyber assaults, data protection through Digital Identity is urgently needed.”
Approximately 82% of organisations encountered at least one data breach due to digital transformation, with an expected 90% of B2C organisations competing based on customer UX by 2024. Additionally, between 2019 and 2021, there was a threefold increase (307%) in account takeover fraud. In the United States alone, the recorded number of data breaches in 2021 reached 4.7 billion, showing a notable 37% rise compared to the previous year.
Such cybersecurity breaches and hacks do not come cheap. The average cost of a security breach in the U.S. increased from US$ 8.2 million to US$ 9.5 million. Moreover, the risk of loss increases from US$ 8.6 million to US$ 10.6 million if the company offers a remote working policy.
“The cost of this violation arises due to the need for detection and escalation, notification to related parties and potential lost business. Not to mention the cost of recovering reputation damage which is difficult to calculate,” Adam explains.
Unauthorised access abuse stands out as one of the most prevalent entry points for this series of hacks and breaches.
Unauthorised access is accomplished through brute-force attacks, phishing, password spraying or other attack methods. This breach allows attackers to find and steal valuable data, such as customer records, intellectual property or financial information.
The top three violations that led to hacks, according to Adam are:
- Unauthorised access. It has been the leading cause of hacking in the U.S. for the fourth year in a row with a 45% increase in 2020
- This is another powerful method that has grown by 24%
- Supply Chain Attacks. Breaches in the distribution chain (supply chain) and third parties are up 22%. Violations of this model seem to be increasingly popular because they have grown 297%, from previously only 126 cases to 500 cases in 2020.
These various intrusions have caused a significant decline in consumer confidence, with more than 82% expressing concerns about how companies collect and utilise their data. This heightened awareness of data privacy has resonated with 74% of U.S. adults, who highly value the security of their personal information.
ForgeRock offers software to secure and personalise user data with various AI-enabled authentication options. ForgeRock Identity Platform helps financial services organisations implement Strong Customer Authentication (SCA) by leveraging contextual signals, such as location, IP address, device type, operating system and browser to trigger SCA at the right time.
“This service eliminates friction when a customer needs to authenticate multiple services at once,” confirms Adam. “ForgeRock Trust Network enables access to a variety of pre-integrated third-party authentication, to address risk/fraud management, behavioural biometrics and identity check solutions (eKYC).”
Power Talk: Reimagining the Future of Smart Nation Citizen Services Through Intelligent Automation
Intelligent automation refers to the convergence of artificial intelligence (AI) and automation technologies, such as robotic process automation (RPA). This powerful combination enables the streamlining and automation of repetitive tasks and processes, enhancing operational efficiency and productivity.
Reimagining the future of Smart Nation citizen services through intelligent automation has the potential to significantly improve service delivery and citizen experience. AI and automation technologies, help personalise services, improve efficiency, provide 24/7 availability, reduce costs and make data-driven decisions to improve service delivery.

Peter Forbes, Group Chief Digital Officer of the National University Health System (NUHS), spoke about their work in this field. “Our organisation is working with dedicated resources from trusted partners who develop and implement these RPA processes.”
During the development phase, a strong focus is placed on comprehensive documentation of the processes. Working closely with their trusted partner, the organisation ensures that the implemented processes are comprehensively compliant. This collaborative approach instils confidence in the organisation, knowing that the automation processes align with the necessary regulatory guidelines, policies and standards.
NUHS initiated the implementation of robotic process automation (RPA) by identifying appropriate use cases within the organisation. The initial emphasis was on the finance department, where RPA was deployed to tackle laborious and time-consuming tasks.
This approach proved particularly valuable in overcoming manpower constraints during the challenging circumstances of the COVID-19 pandemic. By leveraging RPA technology, NUHS achieved notable improvements in operational efficiency and effectively addressed resource limitations in a rapidly changing environment.
Automation facilitated tasks such as data input into systems and enabled the timely completion of essential operations that would have otherwise been challenging to accomplish within the given timeframe.
Peter further highlighted that the automation initiatives at NUHS extended beyond the finance department and encompassed various operational areas. An example is the automation of home delivery processes in the pharmacy department. The manual effort and overtime work required for home deliveries were alleviated through automation, resulting in positive feedback from pharmacy staff who no longer had to work extended hours.
The organisation faced challenges related to budgeting, as the annual budgeting process required planning automation projects a year in advance, Peter shared. To address this, a central budget pool was established in collaboration with the IT office. This allowed users to draw from the central pool and allocate the funds to their department budgets, providing more agility in funding automation initiatives.
The organisation is interested in learning about similar experiences and strategies employed by other customers.
Implementing automation within an organisation helps alleviate high workloads and maintain service quality for patients or customers. By automating repetitive tasks, employees can focus on more meaningful interactions, such as patient care.
Automation fills gaps in the workforce and improves efficiency. For instance, in materials management, automation handles tasks like tracking inventory, reordering, and invoicing, reducing human involvement and streamlining the process.
Spreading automation successes helps promote its benefits and recognises staff involvement. It is important to continuously promote and reward automation efforts, overcoming the challenge of busy schedules and ensuring commitment to automation initiatives.
“Our organisation values showcasing good automation practices to provide recognition and incentivise further investment,” Peter concludes.

Dan Ternes, Chief Technology Officer, SS&C Blue Prism acknowledges that legacy systems pose a significant challenge in organisations, as the expectation of replacing them with new digital systems often proves unrealistic.
“Despite the initial belief that legacy systems would be phased out within a few years, the reality is that many organisations still have a backlog of these outdated applications,” Dan says. “Replacing systems such as patient records, immigration systems, or core banking systems is not feasible within a short timeframe.”
However, the need for process improvements and digital advancements remains. Automation serves as a solution to bridge the gap between legacy systems and digital transformation. It enables organisations to make improvements and automate processes within the existing infrastructure, even if the underlying systems are outdated. Automation provides a practical approach to achieving efficiency and digitalisation despite the presence of legacy systems.
Change for the sake of change or changes that personally affect individuals is often met with resistance. However, people are generally open to change, provided that the change is beneficial to them. It is important to demonstrate how the change will positively impact individuals and their jobs. While people appreciate meaningful and engaging work, they also value job security and stability.
While the pandemic forced transformation, or at least accelerated pre-existing plans, most organisations had strategies in place. It is pertinent to note that there were advocates for automation and digital transformation even before COVID-19.
“Many people were initially sceptical and hesitant to take risks, but the pandemic forced organisations to adopt automation as a necessity,” says Dan.
The crisis opened their eyes to the effectiveness and scalability of automation, leading to the emergence of champions who recognise its value. COVID-19 accelerated the adoption of automation and created opportunities for growth and improvement.
Intelligent automation offers two significant value propositions: operational excellence and innovation. Operational excellence focuses on improving existing processes, while innovation involves exploring new possibilities and creating new products or services.
Organisations often prioritise cost reduction, but they also appreciate business cases that demonstrate new revenue streams, citizen engagement and enhanced customer experiences. Examples of automation success include call centre optimisation and streamlining onboarding processes through OCR and system updates.
Organisations typically progress from automating finance processes to more mission-critical ones and then explore AI integration for transformative purposes. While automation can prove successful in small-scale labs, scaling up to serve millions of customers poses challenges.
The volume of data and the organisation’s capacity to handle it effectively becomes a crucial factor. Digital workers play a significant role in addressing these challenges and facilitating the management of increased workloads.
Dan emphasised that the primary focus of automation initiatives is to automate processes that have a direct impact on consumers and enhance their overall experience. This underscores the organisation’s commitment to prioritising consumer-centricity in automation efforts.
By placing citizens and clients at the forefront, organisations ensure that automation initiatives are aimed at delivering tangible benefits and improving services for the individuals they serve. This approach reflects a strong dedication to enhancing the overall satisfaction and experience of citizens and clients through the strategic implementation of automation technologies.
“Automation offers an opportunity to bridge the gap between legacy systems and digital applications, serving as a temporary solution until system upgrades can be implemented. Hence, organisations recognise the need to solve present-day problems while preparing for future digital transformation,” Dan concludes.
















