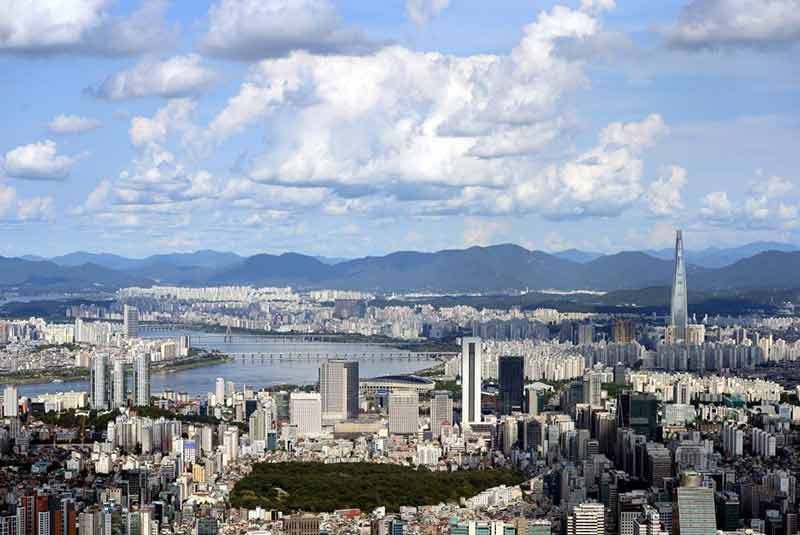
Seoul, the capital city of South Korea, has been conferred the Lee Kuan Yew
World City Prize 2018.
The Lee Kuan Yew World City Prize has been jointly organised by the Urban
Redevelopment Authority (URA) of
Singapore and the Centre for Liveable Cities (CLC)
since 2010. It is a biennial international award that that recognises their cities
and their key leaders and organisations for displaying foresight, good
governance and innovation in tackling the many urban challenges faced, to bring
about social, economic and environmental benefits in a holistic way to their
communities. The nominating
committee includes Dr Cheong Koon Hean, Chief Executive Officer, Housing
& Development Board, Singapore and Prof Kishore Mahbubani, Former Dean, Lee
Kuan Yew School of Public Policy, National University of Singapore.
The jury citation states that Seoul is recognised as the
role model for megacities with a will to change. The city has successfully turned itself around from a highly
bureaucratic top-down city with rising tensions between the government and its
people, into the inclusive, socially stable, and highly innovative city of
today.
Seoul’s successful and impactful high-quality projects to
repurpose urban infrastructure, make the city an excellent example of bold
leadership, commitment to citizen engagement, data-supported problem-solving
decisions, and creative designs to transform the built environment, add
vibrancy and improve quality of life.
Challenges
Nominating Committee Chairman Professor Kishore Mahbubani
said that Seoul once appeared as a city drowning in problems beyond solutions.
However, through a combination of visionary leadership and
active engagement of its citizens, Seoul has turned things around to become an
inclusive, creative and sustainable city with a high quality of life.
Like many other cities experiencing rapid urbanisation,
Seoul found itself confronting many urban challenges at its peak. For instance,
the city was facing the task of providing for a burgeoning car-based society,
which in turn led to other issues such as environmental degradation.
Moreover, prior to the city’s democratisation in the 1990s, citizens
had been largely excluded development decisions and post-democratisation the government
faced resistance from an increasingly vocal citizenry who had lost trust.
The city recognised that its relentless pursuit of economic
success over a relatively short period of time was taking a toll on the quality
of life, which could make the city lose its appeal quickly.
These problems were overcome through the election of
successive visionary leaders in the 2000s who demonstrated strong political
will and displayed foresight to implement a series of catalytic projects – such
as Dongdaemun Area Regeneration to shift Seoul’s focus from traditional
manufacturing to design – that would bring about benefits for the entire city.

Successful strategies
Regaining citizens’
trust
The city leaders understood that proper communication would
be essential to achieve buy-in from both the people and stakeholders. The city
administration undertook rigorous engagement and negotiation with conflicting
parties representing various interests in the city, on issues such as traffic
disturbance, business losses, and historic restoration.
The city formulated a set of conflict management strategies,
which eventually led to a dedicated team of negotiators within the Seoul
Metropolitan Government today for urban development projects, to engage
citizens on the city’s vision. This became the city’s “modus operandi” in urban
development projects. These strategies helped the city achieve impactful and
effective results, and this process in turn helped win over even the most
reluctant citizens over a period of time.
.jpg)
The Seoul Master Plan 2030 under the leadership of current mayor,
Park Won-soon went further to make citizen participation the norm of all plans,
and prioritised bottom-up processes. Ground-up processes are incorporated
in the day-to-day operations under the Community Governance Project where
residents are given a say over local issues that affect their communities
directly.
Citizens can also decide the use of up to 5 percent of the
entire city budget under the Public Participatory Budget System. Through
regular monitoring and publishing of results in the press, and use of big data
in its decision-making to focus on minute details, the city has ensured utmost
transparency and ensured that no citizens are left out.
Through these steps, the city managed to build trust with
the citizens, and also assured them that engagement is not merely a token
gesture, but one that will truly shape and reshape the future of the city.
Achieving social sustainability is expected to become a much
bigger challenge than extending economic and environmental sustainability, as
cities become larger and more difficult to manage. By making citizens the
creators of their own city plan, Seoul has demonstrated that a truly bottom-up
city is possible, where the citizens own their shared city. This also ensures
that beneficial policies are built upon, as decisions are no longer top-down
and dependent only on the government and experts.
People, not cars
In its urban core areas, Seoul has demonstrated boldness in
shifting away from car-oriented transportation to people-centric spaces. The city
recognises that the transition from private cars to mass transit is not an
overnight task and tackles this through a comprehensive set of measures,
including the use of big data, to make public transport as seamless and
convenient as possible.
Elevated highways and main roads were reclaimed to become
prominent public spaces. For instance, an elevated highway at Cheonggyecheon was
removed to restore a former stream and a natural recreational haven was created
at Cheonggyecheong, while a formerly congested area at Yonsei-ro was
pedestrianised.
.jpg)
The conversion of the Seoul Station Overpass into Seoullo
7017 – a 1 kilometre-long lushly planted elevated walkway with pockets of
activities along the way – demonstrates the city’s commitment to a future where
people come first, not cars.
Development without
demolition
As megacities continue to mature and age, deterioration of its urban
infrastructure is inevitable. Seoul has adopted an innovative approach to
rejuvenate its modern heritage, through a policy termed “development without
demolition”.
The jury stated in its citation that projects like Makercity
Sewoon – a rehabilitation of seven commercial superblocks built in the 1970s
through the sensitive insertion of new interventions and uses, and Mapo Culture
Depot – a conversion of disused oil tanks into a cultural venue and public
space, offer new perspectives in repurposing infrastructure while preserving
collective memories of the people.
Special mention
cities
Four
Special Mention cities were also awarded for their best practices in city
management:
1. Hamburg, Germany
2. Kazan, Russian Federation
3. Surabaya, Indonesia
4. Tokyo, Japan
Hamburg was recognised for overcoming planning challenges to
become an attractive and welcoming city of opportunities for a population that
now includes a growing number of immigrants. It has effectively evolved from
the previous conventional practice of urban expansion on the fringe to a
successful implementation of its inner city densification strategy to cater to
increased demand for housing and urban mobility from its growing population. The
city’s culture of cooperation, as characterised by public-private partnerships
realising many housing and transportation projects, and complemented by a
citizen participation process that acknowledges its people as key stakeholders
and drivers of change, was also commended.

Kazan has been recognised for its turnaround from a formerly
drab city with youth criminal gang and poor public health problems into a
healthy city now known for sports and social and religious harmony. The city has
invested strategically in sports, medicine, nutrition, and family life to
improve Kazan’s overall quality of life.
The city capitalises on its youth, as seen in its young
leadership, and it is committed to bringing new ideas that could catalyse
positive change. Kazan is one of the host cities for the 2018 FIFA World Cup in
Russia, as well as the host for the 2019 WorldSkills Competition. These events
provide the impetus for infrastructural upgrades and urban development that
will benefit the everyday life of its residents.
Surabaya’s ‘Kampung Improvement Programme’ successfully
brought together strong community support and participation from the citizens
to collaborate closely with the local government in transforming the kampungs
into clean, conducive, and productive environments. As part of the programme, the
city provided professional training to improve the villagers’ in-house
production of food and crafts for sale, made available cheap credit by the
national government, and prepared the market to absorb the products.

The ‘Kampung Unggulan’ (Prominent Kampung) and ‘Pahlawan
Ekonomi’ (Economy Hero) programmes, and community-based waste management
measures such as recycling, composting and waste bank helped to formalise and
improve the economic status of the lower income settlements, transforming their
subsistence economy into urban economy, while also promoting home-based entrepreneurship.
The jury also highlighted Mayor Tri Rismaharin’s inclusive
and people-centric urban development approach to advance Surabaya from an
unattractive city into a clean and green thriving metropolis with improved
quality of life.
Tokyo has been recognised for the implementation of the
city’s urban blueprint first developed in 2001 and updated in 2016, through which
Tokyo has transformed from its low period of the 90s following the burst of
Japan’s economic bubble to the highly efficient, liveable, and vibrant city one
experiences today. The press release states that the Japanese concept of
“kaizen” through its long-term provision of, and continuous investment in, its
public transportation network over 60 years to ensure its contemporary
efficiency and success.
Tokyo was also praised for its exceptional public-private
partnership model, wherein it overcomes its governance and budget limitations
by leveraging the enlightened private sector with the capability and talents to
deliver high quality urban development projects.