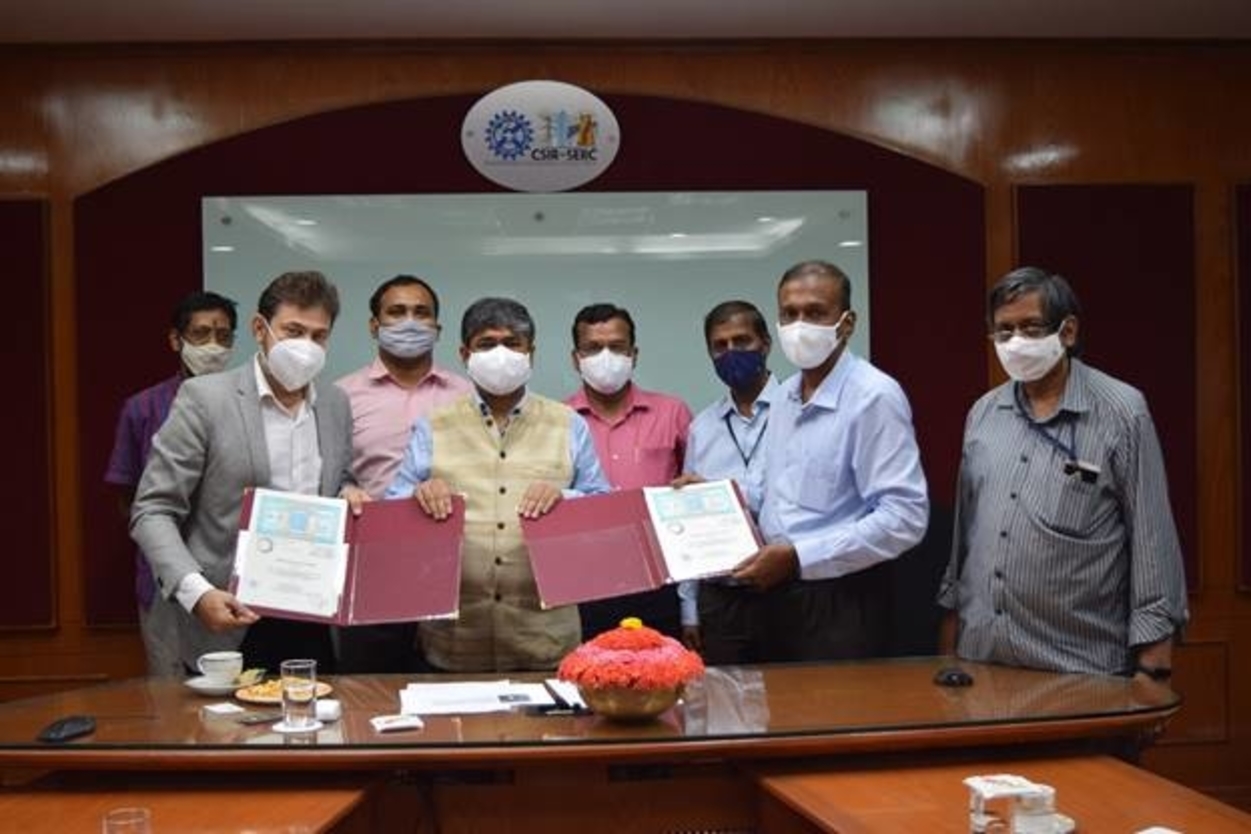
The Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) constituent’s laboratory, the Structural Engineering Research Centre (SERC) has developed the emergency retrieval system (ERS). It allows for the quick retrieval of power transmission in the event of the failure of transmission line towers.
According to a press release, CSIR-SERC, which is based in Chennai, has signed an agreement for licensing of the ERS technology with Advait Infratech, Ahmedabad.
At present, the ERS systems are imported. There are very few manufacturers across the world and the cost is relatively high. This technological development will enable manufacturing in India for the first time, which will be an import substitute and will cost about 40% of imported systems. ERS has a huge market requirement in India as well as in SAARC and African countries. Hence, this technological development is a big leap forward towards Atma Nirbhar Bharat and Make in India, two of the government’s flagship programmes.
ERS is a lightweight modular system that is used as a temporary support structure to restore power immediately after the collapse of transmission line towers during natural calamities such as cyclones or earthquakes, or manmade disruptions. ERS can be assembled quickly at the disaster site for restoration of power in 2-3 days, whereas the permanent restoration may take several weeks. This development is very significant as the failure of transmission lines severely impact lives and causes huge monetary loss to the power companies. As the total losses/damages are directly proportional to the outage duration, time is a crucial factor in reinstating or remediating the damaged/fallen structures, the release noted.
Made of structurally highly stable box sections, ERS is lightweight, modular, and reusable. It provides a complete solution from member connections up to the foundation for different types of soil conditions. The system is verified through rigorous structural tests. Basic knowledge and tools are enough to assemble and install ERS at the disaster site. Suitable configurations for different voltage-class of transmission line systems are possible. The system is compact and yet provides full functionality on erection. It is designed as a scalable system for 33 to 800 kV class of power lines and can help build a disaster-resilient society.
Last month, The Union Cabinet gave its approval for signing a memorandum of cooperation (MoC) between India and Japan on bilateral cooperation in the field of information and communication technologies (ICTs), including public protection and disaster relief.
Further, the MoC will help in cooperation between two countries in various fields like 5G network, telecom security, submarine cable, certification of communication equipment, utilisation of latest wireless technologies, ICT capacity building, artificial intelligence, blockchain, spectrum chain, spectrum management, and cooperation on multilateral platforms.
The pact will contribute to strengthening bilateral cooperation and mutual understanding in the field of communications and will serve as a strategic initiative for India as Japan is an important partner with “special strategic and global partnership” status.
Governments rely on several, specific systems that often work in isolation from each other for critical event management. According to world experts in Critical Event Management, Everbridge, this approach can create duplication in information and processes, data contradictions, and could lead to loss of life and damages.
Unlike fragmented or homegrown tools, Everbridge offers the most proven modern public warning platform which delivers best of breed capabilities to help governments and public authorities keep people safe before, during, and after critical events, anytime and anywhere in the world. The Everbridge Public Warning platform delivers the most comprehensive, flexible, and modular solutions for population alerting to suit the needs of each city, state, or country.