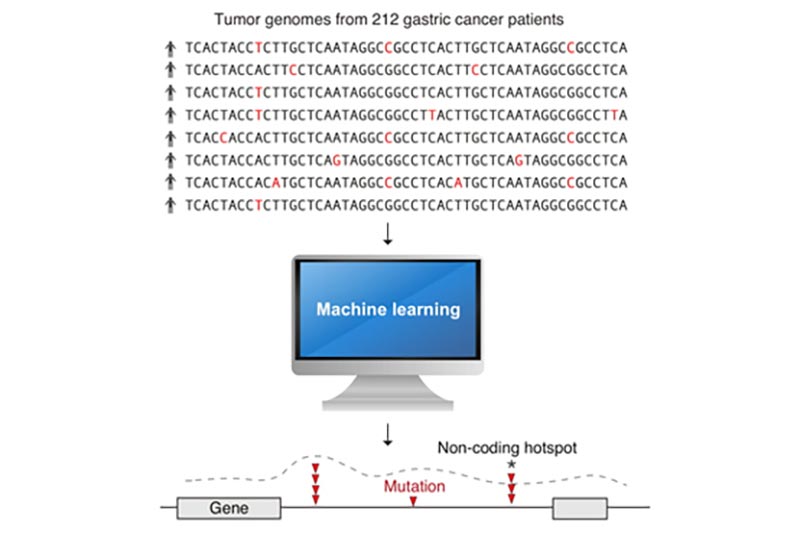
Scientists at A*STAR’s Genome Institute of Singapore (GIS)
have developed
new machine learning computer models to accurately pinpoint cancer mutations.
They have also discovered new mutations in non-coding DNA (specifically, DNA
that does not encode for proteins) which may cause gastric cancer, utilising computational
and data-driven approaches.
Furthermore, the innovative methods and technology developed
through this study will aid researchers in understanding the impact of
mutations in non-coding DNA in other cancer types.
According to statistics from
the World Health Organisation (WHO), cancer is one of the leading causes of
death worldwide and gastric cancer or stomach cancer is the fourth most lethal
cancer in the world. It arises from mutations in the DNA that lead to
abnormal cell growth.
Only two percent of DNA comprises our genes and most studies
have focused on this portion of the DNA. A lot has been learnt about cancer
through the study of this two percent. But there is increasing evidence that mutations
in the remaining 98%, termed non-coding DNA, which regulates the activity of the
genes, can also contribute to cancer.
In this project, two new artificial intelligence (AI)
methods were created to scan the entire genomes (the sum total of DNA within a
single cell of an organism is the genome) of 212 gastric cancer tumours in a
few months. The analysis would have otherwise taken 30 years to complete on a
standard modern computer.
Using computer clusters at GIS and the National
Supercomputing Centre (NSCC) Singapore, the analysis uncovered several new
cancer-associated mutation hotspots located throughout the genome. It also
provided new evidence that mutations in the non-coding DNA may cause cancer by
altering the 3-dimensional (3D) genome structure.
The findings suggest that mutations at 11 non-coding sites
regulating the 3D genome structure are extremely frequent. Approximately one in
every four gastric cancer patients have mutations at these specific sites.
Dr Anders Skanderup, Principal Investigator at GIS and lead
scientist of the study, said, “These non-coding mutations are also frequent in
other types of gastrointestinal cancers such as colorectal, pancreatic and
liver cancer. Therefore, they can be used as biomarkers to detect and monitor
the progression of gastrointestinal cancers too.”
Professor Patrick Tan, Director of Singhealth Duke-NUS
Institute of Precision Medicine (PRISM), Deputy Executive Director of A*STAR’s
Biomedical Research Council, and co-lead scientist commented, “Sophisticated
machine learning techniques such as the one developed in this study are
absolutely essential towards decoding the information encoded in our genomes.
If experimentally validated, these findings point towards a mechanism of cancer
development missed by previous studies.” Professor Tan is also a professor at
the Cancer & Stem Cell Biology Programme in Duke-NUS Medical School.
Professor Ng Huck Hui, Executive Director of GIS, said,
“Previous studies focus solely on profiling mutations in the protein coding
regions of our DNA, which makes up a mere two percent of our DNA. So, it has
been an open question for ages whether we are missing vital information by
overlooking the other vast 98%. This is the first study investigating the
impact of non-coding DNA mutations in gastric cancer and we anticipate that it
will inspire new research to further uncover the mechanisms and impact of these
specific mutations.”
These results were published in Nature Communications
on 18 April 2018.
















