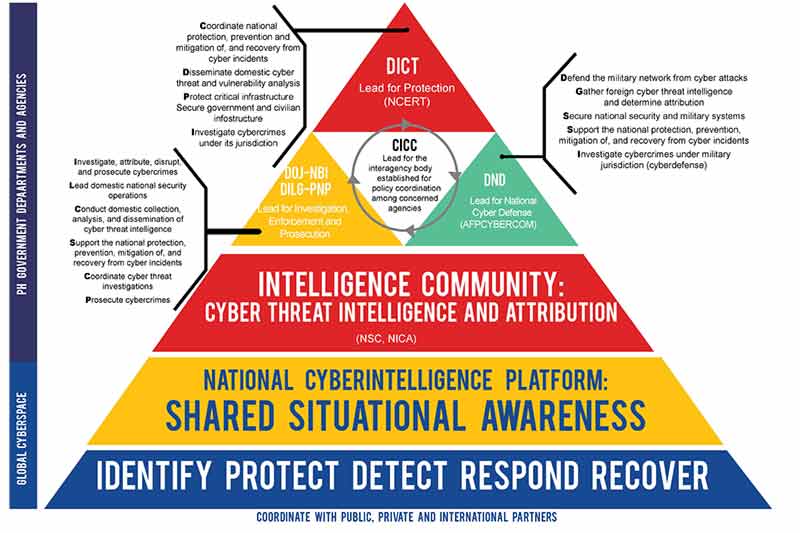
National Cybersecurity Framework (Abbreviations- NCERT: National Computer Emergency Response Team; DOJ-NBI: Department of Justice-National Bureau of Investigation; DILG-PNP: Department of the Interior and Local Government- Philippine National Police; DND: Department of National Defense; NSC: National Security Council; NICA: National Intelligence Coordinating Agency)/ Source: NCSP 2022
The Department of Information and Communications Technology (DICT) in Philippines released the National Cybersecurity Plan 2022 (NCSP) on May 2. As Philippines embarks on an ambitious digital transformation programme, cybersecurity will play a critically important role.
DICT is mandated to “ensure the rights of individuals to privacy and confidentiality of their personal information; ensure the security of critical ICT infrastructures including information assets of the government, individuals and businesses; and provide oversight over agencies governing and regulating the ICT sector and ensure consumer protection and welfare, data privacy and security, foster competition and the growth of the ICT sector.”
The NCSP is intended to shape the policy of the government on cybersecurity and the crafting of guidelines that will be adapted down to the smallest unit of the government. It is also expected to provide a coherent set of implementation plans, programmes, and activities to be shared with all stakeholders.
The primary goals of NCSP 2022 include: (1) assuring the continuous operation of the Philippines’ critical infostructure (CII), and public and military networks; (2) implementing cyber resiliency measures to enhance ability to respond to threats before, during, and after attacks; (3) effective coordination with law enforcement agencies; and (4) a cybersecurity-educated society.
Key strategic initiatives
Protecting CII
As mentioned previously, one of the core areas is protection of CII, CII being defined as "critical infostructure whose failure or limited operation due to natural or man-made disasters would surely cause a tremendous impact on the majority of citizens." NCSP 2022 expands upon a list from 2001 and adopts the CII list from the Cybersecurity Strategy of Singapore. The list includes, but not limited to government and emergency services, business process outsourcing, healthcare, media, banking, lìnancial, power, water, telecommunications, transport and logistics.
In order to establish the baseline for cybersecurity capability and capacity in the protection of CII, the government will focus on compliance and assessment, conduct National Drill Exercises and establish a National Database for Monitoring and Reporting, as a common source of threat reports, including intrusion attempts and other computer incidences. Reporting of security breaches and intrusion attempts will be mandatory for all government agencies.
Compliance and assessment in turn shall comprise three levels: 1) Protection Assessment, 2) Security Assessment and 3) Compliance to Cyber Risks to CII. Levels 1 and 2 shall become a standard practice and will work as complementary to the Information Systems Strategic Plan (lSSP) of government agencies, which offers the blueprint of the digital environment. Level 3 on the other hand is a voluntary program where government agencies may be assessed by a third party institution, such as a Certifying Body that promotes compliance to standards.
National Drill Exercises will be mandatory for all government agencies, with the aim of sustaining the development of cybersecurity towards high maturity levels. At the lowest level of ‘Reactive and Manual’ the primary concern is to putting out fires, as and when they are detected. The ultimate objective is the ‘Resilient Enterprise’ state, with predictive and mission-focused systems and processes to isolate and contain damage, secure supply chains, and protect CII.

Protection of government networks
A National Computer Emergency Response Program will be established and guidelines formulated to aid government agencies in the event of a cyberattack or cyber incidents, including prolonged cyberattacks. NCSP states that the emergency protocol should become part of the operational environment of government agencies, right down to local government units. The protocols will include a Computer Emergency Strategic Communications Plan. This shall form part of the periodic National Drill Exercises.
NCSP recommends the establishment of Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) positions in government agencies. The general responsibilities of a CISO would include using information security measures for policy, resource allocation, and budget decisions.; documenting remedial actions to address any deficiencies in the information security policies, procedures, and practices of the agency, obtaining adequate financial and human resources; ensuring that a standard process is used throughout the agency for information security measures development, creation, analysis, and reporting and reporting on security measures to the CIO.
The NCSP delineates the hierarchy of the Computer Emergency Response Program. It will be composed of the National CERT, Government CERTs, Sectoral CERTs, and Military CERTs. The National CERT will be the highest body for cybersecurity related activities. The Department of National Defense (DND) will be in charge of establishing and operating the Military CERT.

NCSP expects that building the capability of the CERT of government agencies will take time. The first step will be to build the awareness and understanding of what to do in the event of the attack, who to report to, and how to deal with the impact during the preparatory stage while the agencies are still in CERT building stage. The government will provide training programs, such as Training of Trainers and Basic Computer Emergency Response.
The government shall engage and collaborate with the academia to support the development of cybersecurity specialists through curriculum development and also maintain a list of Information Security and Cybersecurity Experts.
One of the long term programmes under the strategy is to establish a Threat Intelligence and Analysis Operations Center to provide a facility to house Research and Development, Testing Laboratories and Threat Scenario Simulators.
NCSP requires that all departments and agencies of the government, the congress, judiciary, state universities and colleges, government owned or controlled corporations to conduct mandatory review of all its existing software licenses, machines and devices to ensure that all necessary components are up to date and are still well within its life cycle period.
Protection for supply chain
The government will employ common criteria to determine compliance of the suppliers and will establish guidelines to conduct benchmarking to ensure that the ICT equipment are compliant with the government’s standards.
Protection of individuals
The government will take a multi-pronged approach to accelerate cybersecurity learning and skills development. Cybersecurity subjects will be integrated into higher education curriculum and apprenticeships and cooperative education programs encouraged to provide an immediate workforce that can earn a salary while they learn the necessary skills.
Strategic relationships will be developed with youth organizations, community- based agencies, and relevant domestic and international private organisations. Outreach programmes will be conducted through print, radio, Internet and television. A National Cybersecurity Awareness Month will be organised.
Institutionalising disparate initiatives and strategies
The NCSP document acknowledges that cybersecurity in Philippines is still in its infancy stage, notwithstanding previous initiatives undertaken through different agencies, including laws that have been promulgated to protect data and information.
It is hoped that NCSP 2022 will provide the roadmap for a coherent and cohesive strategy for cybersecurity and help integrate and institutionalise all the initiatives and strategies that have already been started by government agencies. It is also expected to address the challenges in mounting a synchronised defense in the event of an attack, by clearly defining roles, functions, objectives and goals.
















