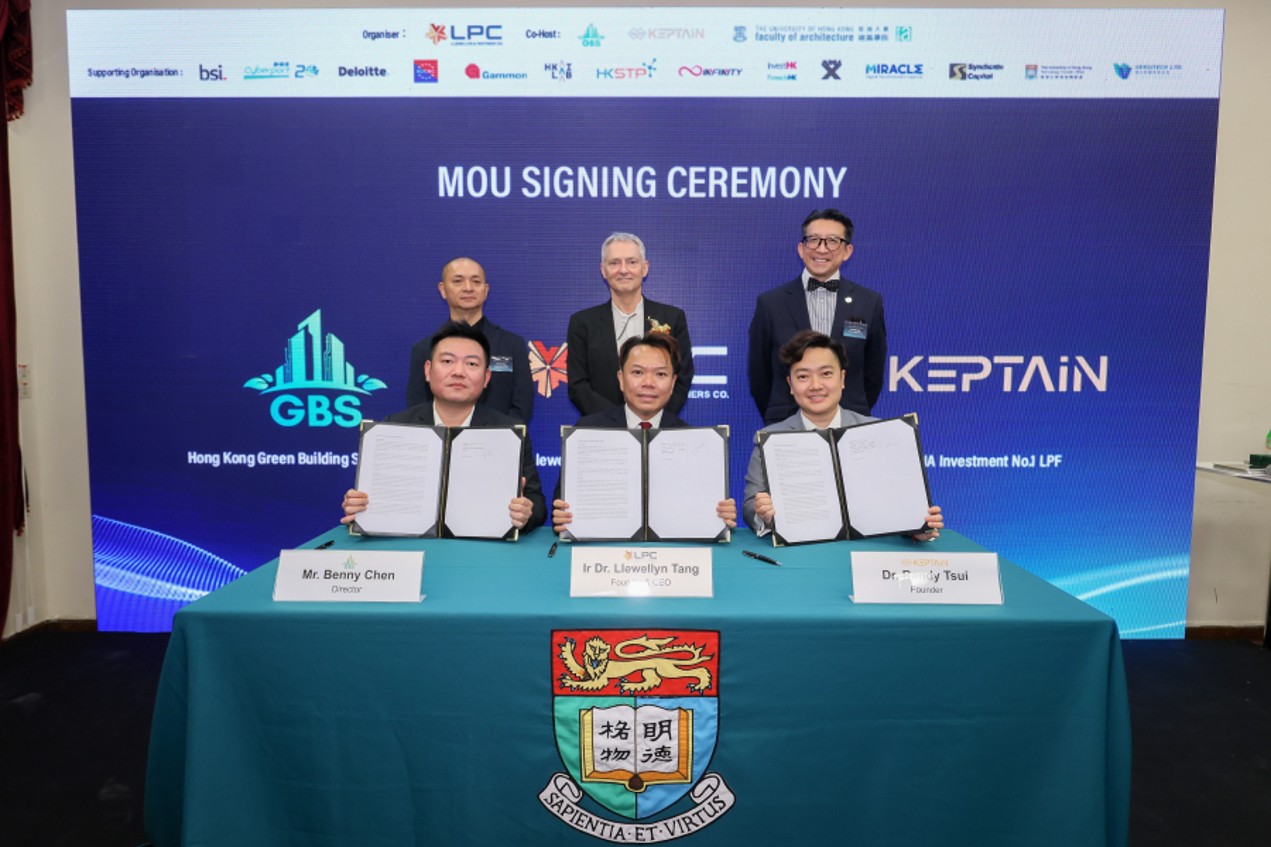
U.S. researchers combined large sets of real-world solar data and advanced machine learning to study the impacts of severe weather on solar farms, and sort out what factors affect energy generation. Their results were published earlier this month in the scientific journal Applied Energy. This research was supported by the Department of Energy’s (DOE) Solar Energy Technologies Office and was conducted in partnership with the National Renewable Energy Laboratory.
Hurricanes, blizzards, hailstorms and wildfires all pose risks to solar farms both directly in the form of costly damage and indirectly in the form of blocked sunlight and reduced electricity output. Two U.S. researchers scoured maintenance tickets from more than 800 solar farms in 24 states and combined that information with electricity generation data and weather records to assess the effects of severe weather on the facilities. By identifying the factors that contribute to low performance, they hope to increase the resiliency of solar farms to extreme weather.
Trying to understand how future climate conditions could impact our national energy infrastructure, is exactly what we need to be doing if we want our renewable energy sector to be resilient under a changing climate. Right now, we are focused on extreme weather events, but eventually we will extend into chronic exposure events like consistent extreme heat.
Senior Researcher
The research team first used natural-language processing, a type of machine learning used by smart assistants, to analyse six years of solar maintenance records for key weather-related words. The analysis methods they used for this study has since been published is freely available for other photovoltaic researchers and operators.
While hailstorms tend to be very costly, they did not appear in solar farm maintenance records, likely because operators tend to document hail damage in the form of insurance claims. Instead, she found that hurricanes were mentioned in almost 15% of weather-related maintenance records, followed by the other weather terms, such as snow, storm, lightning and wind.
The lead author on the paper stated that some hurricanes damage racking — the structure that holds up the panels — due to the high winds. The other major issue they have seen from the maintenance records and talking with our industry partners is flooding blocking access to the site, which delays the process of turning the plant back on.
The researchers combined more than two years of real-world electricity production data from more than 100 solar farms in 16 states with historical weather data to assess the effects of severe weather on solar farms. They used statistics to find that snowstorms had the highest effect on electricity production, followed by hurricanes and a general group of other storms. Then they used a machine learning algorithm to uncover the hidden factors that contributed to low performance from these severe weather events.
The lead author said that statistics gives part of the picture, but machine learning was really helpful in clarifying what are those most important variables. The researchers ended up with a suite of variables and machine learning was used to hone in on the most important ones. The team found that across the board older solar farms were affected the most by severe weather. One possibility for this is that older solar farms had more wear-and-tear from being exposed to the elements longer
The researchers are currently expanding this work to look at the effects of severe weather on the entire electrical grid, add in more production data, and answer even more questions to help the grid adapt to the changing climate and evolving technologies.